Prognostic significance of red cell distribution width in bladder cancer
- PMID: 32420135
- PMCID: PMC7215002
- DOI: 10.21037/tau.2020.03.08
Prognostic significance of red cell distribution width in bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. It ranks ninth among all cancers and fourth among cancers in male patients. Recent studies reported that red blood cell (RBC) distribution width (RDW) was a potential predictor in some cancers. This study explored the significance of RDW in patients with bladder cancer after radical cystectomy.
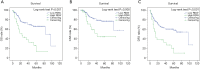
Methods: This study involved 169 patients who underwent radical cystectomy between March 2009 and October 2018. The overall survival (OS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and disease-free survival (DFS) were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were used to evaluate the prognostic significance of RDW.
Results: The patients with bladder cancer were divided into two subgroups according to the RDW value (0.1395). A high RDW value significantly correlated with higher mortality, a decrease in hemoglobin, an increase in C-reactive protein, a decrease in RBC count, and T stage (P<0.05). Statistically significant differences in OS, CSS, and DFS were found between high- and low-RDW groups. Hence, a high RDW value was presumed to be a risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with bladder cancer after radical cystectomy (P<0.001).
Conclusions: Patients with a high RDW value had a poor prognosis. Therefore, RDW is a reliable predictor for the prognosis of patients with bladder cancer who underwent radical cystectomy.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; prognosis; radical cystectomy; red blood cell distribution width (RDW); systemic inflammation.
2020 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau.2020.03.08). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials