Retroperitoneal single-site robot-assisted partial nephrectomy using Lapsingle Vision advanced access platform: initial three case reports
- PMID: 32420181
- PMCID: PMC7215040
- DOI: 10.21037/tau.2020.01.14
Retroperitoneal single-site robot-assisted partial nephrectomy using Lapsingle Vision advanced access platform: initial three case reports
Abstract
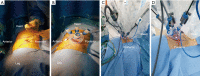
Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy is currently the standard for treatment of small renal mass. Recently, robot-assisted single site surgery has been introduced. However, there have been few reports of retroperitoneal approaches. Herein, we report initial case series of retroperitoneal single-site robot-assisted partial nephrectomy using the da Vinci Xi surgical system using the Lapsingle Vision advanced access platform. Three patients have undergone retroperitoneal single-site robot-assisted partial nephrectomy due to incidental finding of renal mass. Operation duration, estimated blood loss, warm ischemia time, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) change, and complication were evaluated. Renal cell carcinoma of the two clear cell type and one chromophobe was diagnosed based on the pathological examination. Initial two cases were successfully completed with minimal bleeding and warm ischemic time within 25 minutes. The last 3rd case has been converted to multiport operation due to limited retroperitoneal space and difficulty in managing upper pole renal mass. Retroperitoneal single-site robot-assisted partial nephrectomy is a feasible treatment modality for treatment of posterior or lateral renal masses. Additional cases are needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of this technique.
Keywords: Kidney cancer; nephrectomy; retroperitoneal; robotics; single site case reports.
2020 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau.2020.01.14). KHR serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Translational Andrology and Urology from Jun 2019 to May 2021. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
