Three months of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32420674
- PMCID: PMC7267122
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2113
Three months of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
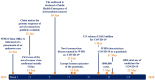
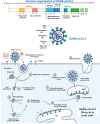
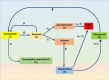
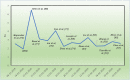
The pandemic of 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2019), reminiscent of the 2002-SARS-CoV outbreak, has completely isolated countries, disrupted health systems and partially paralyzed international trade and travel. In order to be better equipped to anticipate transmission of this virus to new regions, it is imperative to track the progress of the virus over time. This review analyses information on progression of the pandemic in the past 3 months and systematically discusses the characteristics of SARS-CoV-2019 virus including its epidemiologic, pathophysiologic, and clinical manifestations. Furthermore, the review also encompasses some recently proposed conceptual models that estimate the spread of this disease based on the basic reproductive number for better prevention and control procedures. Finally, we shed light on how the virus has endangered the global economy, impacting it both from the supply and demand side.
Keywords: ACE-2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV; mathematical modeling; pandemic.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome‐related coronavirus: the species and its viruses‐a statement of the coronavirus study group. bioRxiv. 2020. 10.1101/2020.02.07.937862. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous