Generating Survival Times Using Cox Proportional Hazards Models with Cyclic and Piecewise Time-Varying Covariates
- PMID: 32421033
- PMCID: PMC7223425
- DOI: 10.1007/s12561-020-09266-3
Generating Survival Times Using Cox Proportional Hazards Models with Cyclic and Piecewise Time-Varying Covariates
Abstract
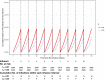
Time-to-event outcomes with cyclic time-varying covariates are frequently encountered in biomedical studies that involve multiple or repeated administrations of an intervention. In this paper, we propose approaches to generating event times for Cox proportional hazards models with both time-invariant covariates and a continuous cyclic and piecewise time-varying covariate. Values of the latter covariate change over time through cycles of interventions and its relationship with hazard differs before and after a threshold within each cycle. The simulations of data are based on inverting the cumulative hazard function and a log link function for relating the hazard function to the covariates. We consider closed-form derivations with the baseline hazard following the exponential, Weibull, or Gompertz distribution. We propose two simulation approaches: one based on simulating survival data under a single-dose regimen first before data are aggregated over multiple-dosing cycles and another based on simulating survival data directly under a multiple-dose regimen. We consider both fixed intervals and varying intervals of the drug administration schedule. The method's validity is assessed in simulation experiments. The results indicate that the proposed procedures perform well in generating data that conform to their cyclic nature and assumptions of the Cox proportional hazards model.
Keywords: Correlates of risk; Joint modeling of longitudinal and survival data; Survival data simulations; Time-dependent covariate; Zero-protection threshold.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNo potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- Mayer KH, Seaton KE, Huang Y, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and immunological activities of multiple intravenous or subcutaneous doses of an anti-HIV monoclonal antibody, VRC01, administered to HIV-uninfected adults: Results of a phase 1 randomized trial. PLoS Med. 2017;14:e1002435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002435. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
