Bayesian regression explains how human participants handle parameter uncertainty
- PMID: 32421708
- PMCID: PMC7259793
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007886
Bayesian regression explains how human participants handle parameter uncertainty
Erratum in
-
Correction: Bayesian regression explains how human participants handle parameter uncertainty.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Mar 3;18(3):e1009932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009932. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35239645 Free PMC article.
Abstract
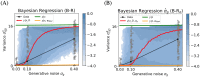
Accumulating evidence indicates that the human brain copes with sensory uncertainty in accordance with Bayes' rule. However, it is unknown how humans make predictions when the generative model of the task at hand is described by uncertain parameters. Here, we tested whether and how humans take parameter uncertainty into account in a regression task. Participants extrapolated a parabola from a limited number of noisy points, shown on a computer screen. The quadratic parameter was drawn from a bimodal prior distribution. We tested whether human observers take full advantage of the given information, including the likelihood of the quadratic parameter value given the observed points and the quadratic parameter's prior distribution. We compared human performance with Bayesian regression, which is the (Bayes) optimal solution to this problem, and three sub-optimal models, which are simpler to compute. Our results show that, under our specific experimental conditions, humans behave in a way that is consistent with Bayesian regression. Moreover, our results support the hypothesis that humans generate responses in a manner consistent with probability matching rather than Bayesian decision theory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures