Multiple-centre clinical evaluation of an ultrafast single-tube assay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA
- PMID: 32422410
- PMCID: PMC7227500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.007
Multiple-centre clinical evaluation of an ultrafast single-tube assay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the performance of an ultrafast single-tube nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection assay for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA using clinical samples from multiple centres.
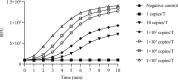
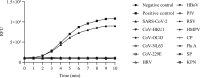
Methods: A reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification (RT-RAA) assay for SARS-CoV-2 was conducted within 15 minutes at 39°C with portable instruments after addition of extracted RNA. The clinical performance of RT-RAA assay was evaluated using 947 clinical samples from five institutions in four regions of China; approved commercial fluorescence quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) kits were used for parallel detection. The sensitivity and specificity of RT-RAA were compared and analysed.
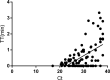
Results: The RT-RAA test results of 926 samples were consistent with those of qRT-PCR (330 were positive, 596 negative); 21 results were inconsistent. The sensitivity and specificity of RT-RAA was 97.63% (330/338, 95% confidence interval (CI) 95.21 to 98.90) and 97.87% (596/609, 95% CI 96.28 to 98.81) respectively. The positive and negative predictive values were 96.21% (330/343, 95% CI 93.45 to 97.88) and 98.68% (596/604, 95% CI 97.30 to 99.38) respectively. The total coincidence rate was 97.78% (926/947, 95% CI 96.80 to 98.70), and the kappa was 0.952 (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: With comparable sensitivity and specificity to the commercial qRT-PCR kits, RT-RAA assay for SARS-CoV-2 exhibited the distinctive advantages of simplicity and rapidity in terms of operation and turnaround time.
Keywords: COVID-19; Detection; Multicentre evaluation; RT-RAA; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang R.Q., Li G.X., Li X.N., Shen X.X., Gao Y., Wang L. A rapid and sensitive recombinase aided amplification assay incorporating competitive internal control to detect Bordetella pertussis using the DNA obtained by boiling. Int J Infect Dis. 2019;86:108–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

