Venous cerebral thrombosis in COVID-19 patient
- PMID: 32422428
- PMCID: PMC7194045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.116871
Venous cerebral thrombosis in COVID-19 patient
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no financial activities related to the present article.
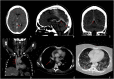
Figures
Comment in
-
Liver abnormality may develop cerebral vein thrombosis in COVID-19.J Neurol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;417:117076. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.117076. Epub 2020 Aug 5. J Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32791424 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia.J Thromb Haemost. 2020 Apr;18(4):844-847. doi: 10.1111/jth.14768. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 32073213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang N., Li D., Wang X., Sun Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020;18(4):844–847. doi: 10.1111/jth.14768. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32073213 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Hajizadeh N., Moore E.E. Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA) Treatment for COVID-19 Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A Case Series. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020 doi: 10.1111/jth.14828. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32267998 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ito T. PAMPs and DAMPs as triggers for DIC. J. Intensive Care. 2014;2(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s40560-014-0065-0. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25705424 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mao L., Jin H., Wang M. Neurological manifestations of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective case series study. JAMA Neurol. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=32275288 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y., Xiao M., Zhang S. Coagulopathy and Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(17) doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2007575. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=32268022 e38. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

