MK2206 Enhances Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Testicular Cancer Through Akt Signaling Pathway Inhibition
- PMID: 32422572
- PMCID: PMC7231864
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100769
MK2206 Enhances Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Testicular Cancer Through Akt Signaling Pathway Inhibition
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "MK2206 enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in testicular cancer through Akt signaling pathway inhibition" [Transl Oncol. 2020 Jul;13(7):100769].Transl Oncol. 2022 Apr;18:101353. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101353. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35152083 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To improve conventional chemotherapeutic efficacy, it is significant to identify novel molecular markers for chemosensitivity as well as possible molecules accelerating cell-killing mechanisms. In this study, we attempted to elucidate how MK2206, an allosteric Akt inhibitor, enhances the cisplatin (CDDP)-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in testicular cancer.
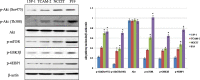
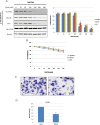
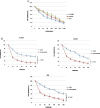
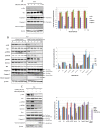
Materials and methods: We checked three testicular cancer cell lines for the expression of phospho(p)-Akt and its downstream molecules targets by Western blot. The potential antitumor effects were analyzed by MTT assay in vitro and by subcutaneous xenograft models in vivo. The cell invasion was analyzed by transwell invasion assay, and the activities of Akt signaling pathway and expression of apoptosis-related proteins were measured by Western blot.
Results: Our results indicated that there was overactivation of p-Akt and its downstream molecules in testicular cancer cell lines compared with normal testis epithelium cells. MK2206 (600 nM) inhibited cell invasion in TCAM-2 and P19 cell lines and significantly increased the susceptibility of testicular cancer to CDDP. Combined with CDDP, MK2206 potentiated CDDP-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis, with repressed expression of p-Akt and its downstream targets. The subcutaneous xenograft models also showed that a combined CDDP/MK2206 therapy completely suppressed tumor growth without any side effects.
Conclusion: These results suggested that the concomitant use of MK2206 could enhance the CDDP-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in testicular cancer with the suppressed expression of Akt pathway.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Datta S.R., Brunet A., Greenberg M.E. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2905–2927. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y., Zhao S., Tian H. Depletion of PI3K p85alpha induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2009;22:1435–1441. - PubMed
-
- Liu N., Rowley B.R., Bull C.O. BAY 80-6946 is a highly selective intravenous PI3K inhibitor with potent p110α and p110δ activities in tumor cell lines and xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:2319–2330. - PubMed
-
- Guerrero-Zotano A., Mayer I.A., Arteaga C.L. PI3K/AKT/mTOR: role in breast cancer progression, drug resistance, and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016;35:515–552. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

