Predictive Value of Early Post-Treatment Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Recurrence or Tumor Progression of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Chemo-Radiotherapy
- PMID: 32422975
- PMCID: PMC7281260
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12051234
Predictive Value of Early Post-Treatment Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Recurrence or Tumor Progression of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Chemo-Radiotherapy
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the predictive capacity of early post-treatment diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for recurrence or tumor progression in patients with no tumor residue after chemo-radiotherapy (CRT) for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and, to assess the predictive capacity of pre-treatment diffusion-weighted MRI for persistent tumor residue post-CRT.
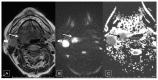
Materials and method: A single center cohort study was performed in one French hospital. All patients with squamous cell carcinoma receiving CRT (no surgical indication) were included. Two diffusion-weighted MRI were performed: one within 8 days before CRT and one 3 months after completing CRT with determination of median tumor apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC).
Main outcome: The primary endpoint was progression-free survival.
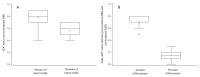
Results: 59 patients were included prior to CRT and 46 (78.0%) completed CRT. A post-CRT tumor residue was found in 19/46 (41.3%) patients. In univariate analysis, initial ADC was significantly lower in patients with residue post CRT (0.56 ± 0.11 versus 0.79 ± 0.13; p < 0.001). When initial ADC was dichotomized at the median, initial ADC lower than 0.7 was significantly more frequent in patients with residue post CRT (73.7% versus 11.1%, p < 0.0001). In multivariate analysis, only initial ADC lower than 0.7 was significantly associated with tumor residue (OR = 22.6; IC [4.9-103.6], p < 0.0001). Among 26 patients without tumor residue after CRT and followed up until 12 months, 6 (23.1%) presented recurrence or progression. Only univariate analysis was performed due to a small number of events. The only factor significantly associated with disease progression or early recurrence was the delta ADC (p = 0.0009). When ADC variation was dichotomized at the median, patients with ADC variation greater than 0.7 had time of disease-free survival significantly longer than patients with ADC variation lower than 0.7 (377.5 [286-402] days versus 253 [198-370], p < 0.0001). Conclusion and relevance: Diffusion-weighted MRI could be a technique that enables differentiation of patients with high potential for early recurrence for whom intensive post-CRT monitoring is mandatory. Prospective studies with more inclusions would be necessary to validate our results.
Keywords: chemo-radiotherapy; diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); head and neck neoplasm; recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fitzmaurice C., Allen C., Barber R.M., Barregard L., Bhutta Z.A., Brenner H., Dicker D.J., Chimed-Orchir O., Dandona R., Dandona L., et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:524–548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buiret G., Combe C., Favrel V., Pommier P., Martin L., Ecochard R., Fayette J., Tartas S., Ramade A., Ceruse P. A Retrospective, Multicenter Study of the Tolerance of Induction Chemotherapy With Docetaxel, Cisplatin, and 5-Fluorouracil Followed by Radiotherapy With Concomitant Cetuximab in 46 Cases of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010;77:430–437. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.04.066. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ceruse P., Cosmidis A., Belot A., Rabilloud M., Fuchsmann C., Poupart M., Ramade A., Tartas S., Favrel V., Pommier P., et al. A pyriform sinus cancer organ preservation strategy comprising induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil, followed by potentiated radiotherapy. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2014;25:970–975. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000126. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

