Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Electrochemical Detection at Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-Printed Electrode
- PMID: 32423013
- PMCID: PMC7287685
- DOI: 10.3390/s20102797
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Electrochemical Detection at Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-Printed Electrode
Abstract
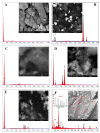
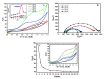
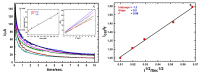
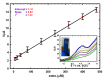
It appeared that either the carbon paste or the screen-printed carbon electrodes that were modified with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) gave rise to the largest current responses after a rapid screening of various nanomaterials as modifiers of carbon composite electrodes in view of designing an electrochemical sensor for Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride (Moxi). The screen-printed electrode (SPE) support was preferred over the carbon paste one for its ability to be used as disposable single-use sensor enabling the circumvention of the problems of surface fouling encountered in the determination of Moxi. The response of AuNPs modified SPE to Moxi was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) (including the effect of the potential scan rate and the pH of the medium), chronoamperometry, and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) after morphological and physico-chemical characterization. DPV was finally applied to Moxi detection in phosphate buffer at pH 7, giving rise to an accessible concentration window ranging between 8 µM and 0.48 mM, and the detection and quantification limits were established to be 11.6 µM and 38.6 µM, correspondingly. In order to estimate the applicability of Moxi identification scheme in actual trials, it was practiced in a human baby urine sample with excellent recoveries between 99.8 % and 101.6 % and RSDs of 1.1-3.4%, without noticeable interference.
Keywords: Moxifloxacin hydrochloride (Moxi); carbon paste electrodes; carbon screen-printed electrodes; differential pulse voltammetry; gold nanoparticles (AuNPs); modified electrodes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A new simple electrochemical Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride sensor built on carbon paste modified with silver nanoparticles.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Jan 15;87:1065-1070. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.077. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 27736686
-
Using Sparfloxacin-Capped Gold Nanoparticles to Modify a Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode Sensor for Ethanol Determination.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 30;23(19):8201. doi: 10.3390/s23198201. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37837031 Free PMC article.
-
Screen-printed disposable electrodes using graphite-polyurethane composites modified with magnetite and chitosan-coated magnetite nanoparticles for voltammetric epinephrine sensing: a comparative study.Mikrochim Acta. 2020 May 10;187(6):318. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-04259-x. Mikrochim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32388628
-
Electrochemical Detection of Sulfadiazine by Sensors based on Chemically Modified Carbon Electrodes: A Review.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(15):1464-1476. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230210115740. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36809949 Review.
-
Recent Progress in Non-Enzymatic Electroanalytical Detection of Pesticides Based on the Use of Functional Nanomaterials as Electrode Modifiers.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 20;12(5):263. doi: 10.3390/bios12050263. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624564 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Sensor Based on ZnFe2O4/RGO Nanocomposite for Ultrasensitive Detection of Hydrazine in Real Samples.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;12(3):491. doi: 10.3390/nano12030491. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159836 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical evaluation of stainless steel alloy as a ureteral stent in synthetic urine solution in-vitro with Candida urinary tract infection.BMC Chem. 2025 Jul 26;19(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01586-z. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 40713696 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical sensing of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) by adapted carbon paste electrode.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 20;14(1):21972. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71341-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39304680 Free PMC article.
-
Metal Nanoparticles and Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Improved Performances of Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors with Biomedical Applications.Materials (Basel). 2021 Oct 22;14(21):6319. doi: 10.3390/ma14216319. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of moxifloxacin in milk using a ratiometric fluorescent sensor based on Ag-MOF@curcumin.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 25;14(19):13482-13488. doi: 10.1039/d4ra00906a. eCollection 2024 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38665504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Omari M.M., Jaafari D.S., Al-Sou’od K.A., Badwan A.A. Moxifloxacin hydrochloride. Profiles Drug Subst. Excip. Relat. Methodol. 2014;39:299–431. - PubMed
-
- Kaur K., Kumar A., Malik A.K., Singh B., Rao A. Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of fluoroquinolones: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008;38:2–18. doi: 10.1080/10408340701804400. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

