Potential therapeutic targets for intracerebral hemorrhage-associated inflammation: An update
- PMID: 32423330
- PMCID: PMC7446569
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X20923551
Potential therapeutic targets for intracerebral hemorrhage-associated inflammation: An update
Abstract
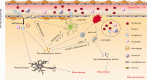
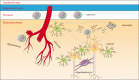
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a subtype of stroke with high mortality and disability but no specific or effective treatment. In the last two decades, much has been learned about the pathologic mechanisms of ICH. It is now known that after ICH onset, immune and inflammatory responses contribute to blood-brain barrier disruption, edema development, and cell death processes, jointly resulting in secondary brain injury. However, the translation of potential therapies from preclinical to clinical success has been disappointing. With the development of new laboratory technology, recent progress has been made in the understanding of ICH pathomechanisms, and promising therapeutic targets have been identified. This review provides an update of recent progress on ICH and describes the prospects for further preclinical studies in this field. Our goal is to discuss new therapeutic targets and directions for the treatment of ICH and promote the effective transformation from preclinical to clinical trials.
Keywords: Intracerebral hemorrhage; immune interventions; inflammation; microglia; secondary injury.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang J, et al.. Inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage: from mechanisms to clinical translation. Prog Neurobiol 2014; 115: 25–44. - PubMed
-
- Jolink WM, Klijn CJ, Brouwers PJ, et al.. Time trends in incidence, case fatality, and mortality of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2015; 85: 1318–1324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

