Comprehensive metabolomics analysis of prostate cancer tissue in relation to tumor aggressiveness and TMPRSS2-ERG fusion status
- PMID: 32423389
- PMCID: PMC7236196
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-06908-z
Comprehensive metabolomics analysis of prostate cancer tissue in relation to tumor aggressiveness and TMPRSS2-ERG fusion status
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PC) can display very heterogeneous phenotypes ranging from indolent asymptomatic to aggressive lethal forms. Understanding how these PC subtypes vary in their striving for energy and anabolic molecules is of fundamental importance for developing more effective therapies and diagnostics. Here, we carried out an extensive analysis of prostate tissue samples to reveal metabolic alterations during PC development and disease progression and furthermore between TMPRSS2-ERG rearrangement-positive and -negative PC subclasses.
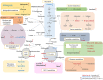
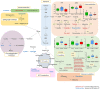
Methods: Comprehensive metabolomics analysis of prostate tissue samples was performed by non-destructive high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (1H HR MAS NMR). Subsequently, samples underwent moderate extraction, leaving tissue morphology intact for histopathological characterization. Metabolites in tissue extracts were identified by 1H/31P NMR and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). These metabolomics profiles were analyzed by chemometric tools and the outcome was further validated using proteomic data from a separate sample cohort.
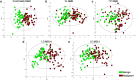
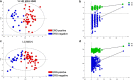
Results: The obtained metabolite patterns significantly differed between PC and benign tissue and between samples with high and low Gleason score (GS). Five key metabolites (phosphocholine, glutamate, hypoxanthine, arginine and α-glucose) were identified, who were sufficient to differentiate between cancer and benign tissue and between high to low GS. In ERG-positive PC, the analysis revealed several acylcarnitines among the increased metabolites together with decreased levels of proteins involved in β-oxidation; indicating decreased acyl-CoAs oxidation in ERG-positive tumors. The ERG-positive group also showed increased levels of metabolites and proteins involved in purine catabolism; a potential sign of increased DNA damage and oxidative stress.
Conclusions: Our comprehensive metabolomic analysis strongly indicates that ERG-positive PC and ERG-negative PC should be considered as different subtypes of PC; a fact requiring different, sub-type specific treatment strategies for affected patients.
Keywords: 1H HRMAS NMR; Gleason score; Metabolomics; Prostate cancer; TMPRSS2-ERG.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Barlow LJ, Shen MM. SnapShot: Prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;24(3):400 e1. - PubMed
-
- Beltran H, Demichelis F. Prostate cancer: Intrapatient heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2015;12(8):430–431. - PubMed
-
- Tian JY, Guo FJ, Zheng GY, Ahmad A. Prostate cancer: updates on current strategies for screening, diagnosis and clinical implications of treatment modalities. Carcinogenesis. 2018;39(3):307–317. - PubMed
-
- Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 2005;310(5748):644–648. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

