Single-cell-resolution transcriptome map of human, chimpanzee, bonobo, and macaque brains
- PMID: 32424074
- PMCID: PMC7263190
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.256958.119
Single-cell-resolution transcriptome map of human, chimpanzee, bonobo, and macaque brains
Abstract
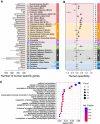
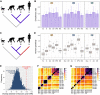
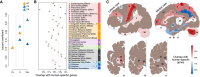
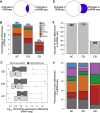
Identification of gene expression traits unique to the human brain sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying human evolution. Here, we searched for uniquely human gene expression traits by analyzing 422 brain samples from humans, chimpanzees, bonobos, and macaques representing 33 anatomical regions, as well as 88,047 cell nuclei composing three of these regions. Among 33 regions, cerebral cortex areas, hypothalamus, and cerebellar gray and white matter evolved rapidly in humans. At the cellular level, astrocytes and oligodendrocyte progenitors displayed more differences in the human evolutionary lineage than the neurons. Comparison of the bulk tissue and single-nuclei sequencing revealed that conventional RNA sequencing did not detect up to two-thirds of cell-type-specific evolutionary differences.
© 2020 Khrameeva et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


References
-
- Barger N, Stefanacci L, Schumann CM, Sherwood CC, Annese J, Allman JM, Buckwalter JA, Hof PR, Semendeferi K. 2012. Neuronal populations in the basolateral nuclei of the amygdala are differentially increased in humans compared with apes: a stereological study. J Comp Neurol 520: 3035–3054. 10.1002/cne.23118 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
