Histone H2A variants alpha1-extension helix directs RNF168-mediated ubiquitination
- PMID: 32424115
- PMCID: PMC7235047
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16307-4
Histone H2A variants alpha1-extension helix directs RNF168-mediated ubiquitination
Abstract
Histone ubiquitination plays an important role in the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway. RNF168 catalyzes H2A and H2AX ubiquitination on lysine 13/15 (K13/K15) upon DNA damage and promotes the accrual of downstream repair factors at damaged chromatin. Here, we report that RNF168 ubiquitinates the non-canonical H2A variants H2AZ and macroH2A1/2 at the divergent N-terminal tail lysine residue. In addition to their evolutionarily conserved nucleosome acidic patch, we identify the positively charged alpha1-extension helix as essential for RNF168-mediated ubiquitination of H2A variants. Moreover, mutation of the RNF168 UMI (UIM- and MIU-related UBD) hydrophilic acidic residues abolishes RNF168-mediated ubiquitination as well as 53BP1 and BRCA1 ionizing radiation-induced foci formation. Our results reveal a juxtaposed bipartite electrostatic interaction utilized by the nucleosome to direct RNF168 orientation towards the target lysine residues in proximity to the H2A alpha1-extension helix, which plays an important role in the DDR pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures

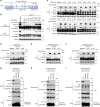



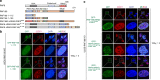
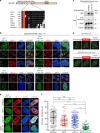
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

