Quantifying genetic effects on disease mediated by assayed gene expression levels
- PMID: 32424349
- PMCID: PMC7276299
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-020-0625-2
Quantifying genetic effects on disease mediated by assayed gene expression levels
Abstract
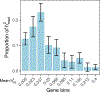
Disease variants identified by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) tend to overlap with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs), but it remains unclear whether this overlap is driven by gene expression levels 'mediating' genetic effects on disease. Here, we introduce a new method, mediated expression score regression (MESC), to estimate disease heritability mediated by the cis genetic component of gene expression levels. We applied MESC to GWAS summary statistics for 42 traits (average N = 323,000) and cis-eQTL summary statistics for 48 tissues from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) consortium. Averaging across traits, only 11 ± 2% of heritability was mediated by assayed gene expression levels. Expression-mediated heritability was enriched in genes with evidence of selective constraint and genes with disease-appropriate annotations. Our results demonstrate that assayed bulk tissue eQTLs, although disease relevant, cannot explain the majority of disease heritability.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Stunnenberg HG et al. The International Human Epigenome Consortium: A Blueprint for Scientific Collaboration and Discovery. Cell 167, 1145–1149 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

