Scalable generalized linear mixed model for region-based association tests in large biobanks and cohorts
- PMID: 32424355
- PMCID: PMC7871731
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-020-0621-6
Scalable generalized linear mixed model for region-based association tests in large biobanks and cohorts
Abstract
With very large sample sizes, biobanks provide an exciting opportunity to identify genetic components of complex traits. To analyze rare variants, region-based multiple-variant aggregate tests are commonly used to increase power for association tests. However, because of the substantial computational cost, existing region-based tests cannot analyze hundreds of thousands of samples while accounting for confounders such as population stratification and sample relatedness. Here we propose a scalable generalized mixed-model region-based association test, SAIGE-GENE, that is applicable to exome-wide and genome-wide region-based analysis for hundreds of thousands of samples and can account for unbalanced case-control ratios for binary traits. Through extensive simulation studies and analysis of the HUNT study with 69,716 Norwegian samples and the UK Biobank data with 408,910 White British samples, we show that SAIGE-GENE can efficiently analyze large-sample data (N > 400,000) with type I error rates well controlled.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS STATEMENT
G.R.A. is an employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. He owns stock and stock options for Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. B.N. is a member of Deep Genomics Scientific Advisory Board, has received travel expenses from Illumina, and also serves as a consultant for Avanir and Trigeminal solutions.
Figures






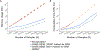
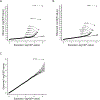
References
METHODS-ONLY REFERENCES
-
- Gilmour AR, Thompson R & Cullis BR Average Information REML: An Efficient Algorithm for Variance Parameter Estimation in Linear Mixed Models. Biometrics 51, 1440–1450, doi: 10.2307/2533274 (1995). - DOI
-
- Davis TA Direct Methods for Sparse Linear Systems (Fundamentals of Algorithms 2). (Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

