Remodeling of light and dark zone follicular dendritic cells governs germinal center responses
- PMID: 32424359
- PMCID: PMC7610477
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-0672-y
Remodeling of light and dark zone follicular dendritic cells governs germinal center responses
Abstract
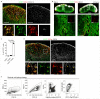
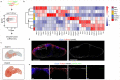
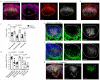
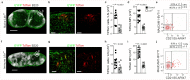
Efficient generation of germinal center (GC) responses requires directed movement of B cells between distinct microenvironments underpinned by specialized B cell-interacting reticular cells (BRCs). How BRCs are reprogrammed to cater to the developing GC remains unclear, and studying this process is largely hindered by incomplete resolution of the cellular composition of the B cell follicle. Here we used genetic targeting of Cxcl13-expressing cells to define the molecular identity of the BRC landscape. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis revealed that BRC subset specification was predetermined in the primary B cell follicle. Further topological remodeling of light and dark zone follicular dendritic cells required CXCL12-dependent crosstalk with B cells and dictated GC output by retaining B cells in the follicle and steering their interaction with follicular helper T cells. Together, our results reveal that poised BRC-defined microenvironments establish a feed-forward system that determines the efficacy of the GC reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

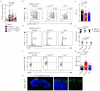


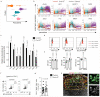
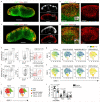

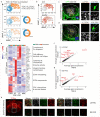
Comment in
-
Directing traffic in the germinal center roundabout.Nat Immunol. 2020 Jun;21(6):599-601. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0690-9. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32424358 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sander S, et al. PI3 Kinase and FOXO1 Transcription Factor Activity Differentially Control B Cells in the Germinal Center Light and Dark Zones. Immunity. 2015;43:1075–1086. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez-Sola D, et al. The FOXO1 Transcription Factor Instructs the Germinal Center Dark Zone Program. Immunity. 2015;43:1064–1074. - PubMed
-
- Shinnakasu R, et al. Regulated selection of germinal-center cells into the memory B cell compartment. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:861–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

