Gallic Acid Impedes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression via Suppression of EGFR-Dependent CARM1-PELP1 Complex
- PMID: 32425504
- PMCID: PMC7186892
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S228123
Gallic Acid Impedes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression via Suppression of EGFR-Dependent CARM1-PELP1 Complex
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a common cause of cancer-related deaths. This study identified the regulatory pattern of gallic acid in NSCLC.
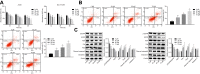
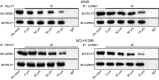
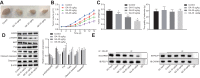
Methods: Human NSCLC cells were treated with different doses of gallic acid, after which, MTT assay and flow cytometry were performed to determine the survival and apoptotic rate of human NSCLC cells. Then, co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed to analyze the relationships between gallic acid, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and CARM1-PELP1. Next, we analyzed whether PELP1, CARM1 and EGFR were associated with the effects of gallic acid on NSCLC cells by conducting rescue experiments. The expression pattern of phosphorylated EGFR, EGFR, Ki67, as well as Fas, FasL and Caspase 3 proteins in cancer cells or xenografts was measured by Western blot analysis. Lastly, the role of gallic acid in the tumor growth was assessed in nude mice.
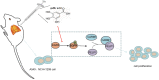
Results: The ideal dose of gallic acid that presented good suppressive effect on NSCLC cells were 30 μM, 50 μM and 75 μM, respectively. Gallic acid played an inhibiting role in the activation of EGFR, which further reduced the formation of CARM1-PELP1 complex, ultimately repressed the proliferation and elevated apoptosis of NSCLC cells. Meanwhile, CARM1 repression led to decreased growth, proliferation and migration abilities of NSCLC cells. Animal experiments confirmed that gallic acid contributed to the inhibition of tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: To sum up, gallic acid could potentially prevent NSCLC progression via inhibition of EGFR activation and impairment of the binding of CARM1 to PELP1, highlighting a novel therapy to dampen NSCLC progression.
Keywords: CARM1; CARM1-PELP1 complex; EGFR; PELP1; gallic acid; non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2020 Wang and Bao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel STAT3 inhibitor W2014-S regresses human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts and sensitizes EGFR-TKI acquired resistance.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):824-840. doi: 10.7150/thno.49600. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391507 Free PMC article.
-
R2-8018 reduces the proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by disturbing transactivation between M3R and EGFR.Life Sci. 2019 Oct 1;234:116742. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116742. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31401315
-
Inhibition of JAK1/2 can overcome EGFR-TKI resistance in human NSCLC.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 18;527(1):305-310. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.095. Epub 2020 May 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32446385
-
Structure and Dynamics of the EGF Receptor as Revealed by Experiments and Simulations and Its Relevance to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cells. 2019 Apr 5;8(4):316. doi: 10.3390/cells8040316. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30959819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How gallic acid regulates molecular signaling: role in cancer drug resistance.Med Oncol. 2023 Sep 27;40(11):308. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02178-4. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37755616 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond Traditional Use of Alchemilla vulgaris: Genoprotective and Antitumor Activity In Vitro.Molecules. 2022 Nov 22;27(23):8113. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238113. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500205 Free PMC article.
-
Gaz Alafi: A Traditional Dessert in the Middle East With Anticancer, Immunomodulatory, and Antimicrobial Activities.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 1;9:900506. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.900506. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35845806 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Health Benefits of Gallic Acid: Therapeutic and Food Applications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 18;13(8):1001. doi: 10.3390/antiox13081001. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting PELP1 Attenuates Angiogenesis and Enhances Chemotherapy Efficiency in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;14(2):383. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020383. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053547 Free PMC article.
-
Gallic Acid Enhances the Efficacy of BCR::ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia through Inhibition of Mitochondrial Respiration and Modulation of Oncogenic Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7958. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147958. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063200 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

