Discovering Selected Antibodies From Deep-Sequenced Phage-Display Antibody Library Using ATTILA
- PMID: 32425512
- PMCID: PMC7218273
- DOI: 10.1177/1177932220915240
Discovering Selected Antibodies From Deep-Sequenced Phage-Display Antibody Library Using ATTILA
Abstract
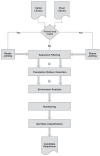
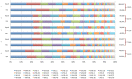
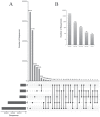
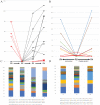
Phage display is a powerful technique to select high-affinity antibodies for different purposes, including biopharmaceuticals. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) presented itself as a robust solution, making it possible to assess billions of sequences of the variable domains from selected sublibraries. Handling this process, a central difficulty is to find the selected clones. Here, we present the AutomaTed Tool For Immunoglobulin Analysis (ATTILA), a new tool to analyze and find the enriched variable domains throughout a biopanning experiment. The ATTILA is a workflow that combines publicly available tools and in-house programs and scripts to find the fold-change frequency of deeply sequenced amplicons generated from selected VH and VL domains. We analyzed the same human Fab library NGS data using ATTILA in 5 different experiments, as well as on 2 biopanning experiments regarding performance, accuracy, and output. These analyses proved to be suitable to assess library variability and to list the more enriched variable domains, as ATTILA provides a report with the amino acid sequence of each identified domain, along with its complementarity-determining regions (CDRs), germline classification, and fold change. Finally, the methods employed here demonstrated a suitable manner to combine amplicon generation and NGS data analysis to discover new monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
Keywords: Phage display; antibody variable domains; biopanning; combinatorial library; next-generation sequencing.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody Isolation from Human Synthetic Libraries of Single-Chain Antibodies and Analysis Using NGS.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2702:347-372. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3381-6_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37679629
-
Construction and molecular characterization of mouse single-chain variable fragment antibodies against Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia pseudomallei.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Feb 28;365(1-2):101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.12.004. Epub 2010 Dec 21. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21172353
-
[Preparation of human phage antibodies specific for SSA/Ro antigen and its sequence analysis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Nov 17;84(22):1904-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15631804 Chinese.
-
[Development of a Rapid Identification Method for a Variety of Antibody Candidates Using High-throughput Sequencing].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(7):823-830. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.16-00252-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017. PMID: 28674295 Review. Japanese.
-
Primer Design and Inverse PCR on Yeast Display Antibody Selection Outputs.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1721:35-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7546-4_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423845 Review.
Cited by
-
New Anti-Flavivirus Fusion Loop Human Antibodies with Zika Virus-Neutralizing Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 15;23(14):7805. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147805. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887153 Free PMC article.
-
Position-Specific Enrichment Ratio Matrix scores predict antibody variant properties from deep sequencing data.Bioinformatics. 2023 Sep 2;39(9):btad446. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad446. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37478351 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning to predict continuous protein properties from binary cell sorting data and map unseen sequence space.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 12;121(11):e2311726121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2311726121. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38451939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grilo AL, Mantalaris A. The increasingly human and profitable monoclonal antibody market. Trend Biotechnol. 2019;37:9-16. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg P, Rader CBI. Analysis of selected antibodies. In: Barbas CF, III, Burton DR, Scott JK, Silverman GJ, eds. Phage Display: A Laboratory Manual. New York: NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2004:736.
-
- Smith GP. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 1985;228:1315-1317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

