Dual Receptor-Targeted and Redox-Sensitive Polymeric Micelles Self-Assembled from a Folic Acid-Hyaluronic Acid-SS-Vitamin E Succinate Polymer for Precise Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 32425522
- PMCID: PMC7188338
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S249205
Dual Receptor-Targeted and Redox-Sensitive Polymeric Micelles Self-Assembled from a Folic Acid-Hyaluronic Acid-SS-Vitamin E Succinate Polymer for Precise Cancer Therapy
Abstract
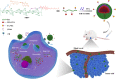
Purpose: Poor site-specific delivery and insufficient intracellular drug release in tumors are inherent disadvantages to successful chemotherapy. In this study, an extraordinary polymeric micelle nanoplatform was designed for the efficient delivery of paclitaxel (PTX) by combining dual receptor-mediated active targeting and stimuli response to intracellular reduction potential.
Methods: The dual-targeted redox-sensitive polymer, folic acid-hyaluronic acid-SS-vitamin E succinate (FHSV), was synthesized via an amidation reaction and characterized by 1H-NMR. Then, PTX-loaded FHSV micelles (PTX/FHSV) were prepared by a dialysis method. The physiochemical properties of the micelles were explored. Moreover, in vitro cytological experiments and in vivo animal studies were carried out to evaluate the antitumor efficacy of polymeric micelles.
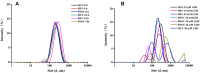
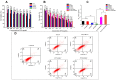
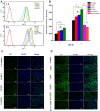
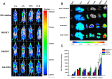
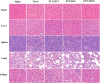
Results: The PTX/FHSV micelles exhibited a uniform, near-spherical morphology (148.8 ± 1.4 nm) and a high drug loading capacity (11.28% ± 0.25). Triggered by the high concentration of glutathione, PTX/FHSV micelles could quickly release their loaded drug into the release medium. The in vitro cytological evaluations showed that, compared with Taxol or single receptor-targeted micelles, FHSV micelles yielded higher cellular uptake by the dual receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway, thus leading to significantly superior cytotoxicity and apoptosis in tumor cells but less cytotoxicity in normal cells. More importantly, in the in vivo antitumor experiments, PTX/FHSV micelles exhibited enhanced tumor accumulation and produced remarkable tumor growth inhibition with minimal systemic toxicity.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that this well-designed FHSV polymer has promising potential for use as a vehicle of chemotherapeutic drugs for precise cancer therapy.
Keywords: antitumor; cytotoxicity; dual-targeted; micelles; paclitaxel; redox-sensitive.
© 2020 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Fen Chen is employed by Zhejiang Jingxin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paclitaxel-loaded redox-sensitive nanoparticles based on hyaluronic acid-vitamin E succinate conjugates for improved lung cancer treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;13:1585-1600. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S155383. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29588586 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting folate-conjugated hyaluronic acid polymeric micelles for paclitaxel delivery.Int J Pharm. 2011 Dec 12;421(1):160-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.09.006. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21945183
-
Intracellular delivery and antitumor effects of a redox-responsive polymeric paclitaxel conjugate based on hyaluronic acid.Acta Biomater. 2015 Oct;26:274-85. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.08.029. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26300335
-
Reduction-responsive polymeric micelles and vesicles for triggered intracellular drug release.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Aug 10;21(5):755-67. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5733. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24279980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodegradable Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Micelles for Treatment of Malignancy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016;17(3):227-36. doi: 10.2174/138920101703160206142821. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26873075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor microenvironment-responsive micelles assembled from a prodrug of mitoxantrone and 1-methyl tryptophan for enhanced chemo-immunotherapy.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2182254. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2182254. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36840464 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-Spectrum Theranostics and Biomedical Application of Functionalized Nanomaterials.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;14(6):1221. doi: 10.3390/polym14061221. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35335551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single- versus Dual-Targeted Nanoparticles with Folic Acid and Biotin for Anticancer Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 3;13(3):326. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030326. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33802531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis and EMT resistance in cancer: a comprehensive review of the interplay.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 26;14:1344290. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1344290. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38469234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic cancer cell membrane-enriched vitamin E-stapled gemcitabine-loaded TPGS micelles for pancreatic cancer therapy.Drug Deliv. 2025 Dec;32(1):2527759. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2025.2527759. Epub 2025 Jul 9. Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40631432 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

