Changes in implementation of personal protective measures by ordinary Japanese citizens: A longitudinal study from the early phase to the community transmission phase of the COVID-19 outbreak
- PMID: 32425637
- PMCID: PMC7231496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.039
Changes in implementation of personal protective measures by ordinary Japanese citizens: A longitudinal study from the early phase to the community transmission phase of the COVID-19 outbreak
Abstract
Objectives: To clarify changes in the implementation of personal protective measures among ordinary Japanese citizens from the early phase of the COVID-19 outbreak to the community transmission phase.
Methods: This longitudinal, internet-based survey included 2141 people (50.8% men; 20-79 years). The baseline and follow-up surveys were conducted from February 25-27, 2020, and April 1-6, 2020, respectively. Participants were asked how often they implemented the five personal protective measures recommended by the World Health Organization (hand hygiene, social distancing, avoiding touching the eyes, nose and mouth, respiratory etiquette, and self-isolation) in the baseline and follow-up surveys.
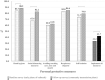
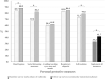
Results: Three of the five personal protective measures' availability significantly improved during the community transmission phase compared to the early phase. Social distancing measures showed significant improvement, from 67.4% to 82.2%. However, the prevalence of avoiding touching the eyes, nose, and mouth, which had the lowest prevalence in the early phase, showed no significant improvement (approximately 60%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that men and persons of low-income households made fewer improvements than women and persons of high-income households.
Conclusions: The availability of personal protective measures by ordinary citizens is improving; however, there is potential for improvement, especially concerning avoiding touching eyes, nose, and mouth.
Keywords: Behavior change; COVID-19; Pandemic; Protective measures; Public health.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (JMHLW) 2020. About coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/newpage_00032.html
-
- Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (JMHLW) 2020. Expert Meeting on the Novel Coronavirus Disease Control Analysis of the Response to the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) and Recommendations (Excerpt)https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000611515.pdf
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

