Associations between NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery and in vivo brain amyloid and tau pathology in non-demented older adults
- PMID: 32426450
- PMCID: PMC7228102
- DOI: 10.1002/dad2.12018
Associations between NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery and in vivo brain amyloid and tau pathology in non-demented older adults
Abstract
Introduction: The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Toolbox Cognition Battery (NIHTB-CB) was developed to be a common assessment metric across a broad array of research studies. We investigated associations between NIHTB-CB and brain amyloid and tau deposition in cognitively unimpaired older adults.
Methods: One hundred eighteen community-based volunteers completed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Pittsburgh compound B (PiB)-PET (positron emission tomography) and AV-1451-PET neuroimaging, a neuropsychological evaluation, NIHTB-CB, and the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) scale. Demographically adjusted regression models evaluated cognition-biomarker associations; standardized effect sizes allowed comparison of association strength across measures.
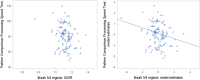
Results: No NIHTB-CB measures were associated with amyloid deposition. NIHTB-CB measures of fluid cognition, including Pattern Comparison Processing Speed, Dimensional Change Card Sort, and Fluid Cognition Composite, were associated with tau deposition in higher Braak regions. Pattern Comparison Processing Speed was the most robust association with sensitivity analyses.
Discussion: NIHTB-CB tasks of processing speed and executive functions may be sensitive to pathologic tau deposition on imaging in normal aging.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; biomarkers; cognition; neuropsychology.
© 2020 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the Alzheimer's Association.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources