Metabolic regulation of kisspeptin - the link between energy balance and reproduction
- PMID: 32427949
- PMCID: PMC8852368
- DOI: 10.1038/s41574-020-0363-7
Metabolic regulation of kisspeptin - the link between energy balance and reproduction
Abstract
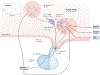
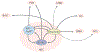
Hypothalamic kisspeptin neurons serve as the nodal regulatory centre of reproductive function. These neurons are subjected to a plethora of regulatory factors that ultimately affect the release of kisspeptin, which modulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) release from GnRH neurons to control the reproductive axis. The presence of sufficient energy reserves is critical to achieve successful reproduction. Consequently, metabolic factors impose a very tight control over kisspeptin synthesis and release. This Review offers a synoptic overview of the different steps in which kisspeptin neurons are subjected to metabolic regulation, from early developmental stages to adulthood. We cover an ample array of known mechanisms that underlie the metabolic regulation of KISS1 expression and kisspeptin release. Furthermore, the novel role of kisspeptin neurons as active players within the neuronal circuits that govern energy balance is discussed, offering evidence of a bidirectional role of these neurons as a nexus between metabolism and reproduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
-
Manfredi-Lozano M, Roa J & Tena-Sempere M Connecting metabolism and gonadal function: novel central neuropeptide pathways involved in the metabolic control of puberty and fertility. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 48, 37–49 (2018).
This study is important in demonstrating the interaction between the melanocortin system and the reproductive axis, indicating that the reproductive action of melanocortins is kisspeptin-dependent.
-
-
- Navarro VM & Tena-Sempere M Neuroendocrine control by kisspeptins: role in metabolic regulation of fertility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8, 40–53 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Goodman RL et al. Kisspeptin neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the ewe express both dynorphin A and neurokinin B. Endocrinology 148, 5752–5760 (2007). - PubMed
-
-
Navarro VM et al. Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion by kisspeptin/dynorphin/neurokinin B neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the mouse. J. Neurosci. 29, 11859–11866 (2009).
The first study demonstrating the concept of kisspeptinARC neurons as the GnRH pulse generator.
-
-
-
Clarkson J et al. Definition of the hypothalamic GnRH pulse generator in mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E10216–E10223 (2017).
This study demonstrates through a series of optogenetic approaches that kisspeptinARC neurons are indeed the GnRH pulse generator.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

