Comparison of Real-Time PCR, Bacteriologic Culture and Fluorescent Antibody Test for the Detection of Leptospira borgpetersenii in Urine of Naturally Infected Cattle
- PMID: 32429076
- PMCID: PMC7356886
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci7020066
Comparison of Real-Time PCR, Bacteriologic Culture and Fluorescent Antibody Test for the Detection of Leptospira borgpetersenii in Urine of Naturally Infected Cattle
Abstract
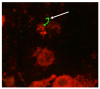
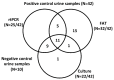
Cattle are susceptible to infection with multiple serovars of pathogenic leptospires, resulting in abortion, stillbirth, premature birth, reproductive failure and milk drop syndrome. Cattle also act as a reservoir host for L. borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo which is excreted from renal tubules via urine into the environment where it persists in suitable moist conditions. Our previous work demonstrated that 7% of urine samples from beef cattle were positive for L. borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo by culture and/or the fluorescent antibody test (FAT). In this study, a real-time PCR (rtPCR) assay was applied to determine the relative performance of rtPCR based detection of L. borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo compared to previously reported culture and FAT techniques. Of 42 bovine urine samples positive for leptospires by culture and/or FAT, 60% (25/42) were positive by rtPCR. Of 22 culture-positive samples, 91% (20/22) were rtPCR-positive. Of 32 FAT-positive samples, 50% (16/32) were rtPCR-positive. For 10 samples that were culture-positive but FAT-negative, 90% (9/10) were rtPCR-positive. For 20 samples that were FAT-positive but culture-negative, 25% (5/20) were rtPCR-positive. Collectively, these results indicate that no single assay is optimal, and the use of more than one assay to detect leptospires in urine from naturally infected cattle is recommended.
Keywords: Leptospira; Leptospirosis; cattle diseases; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Faine S., Adler B., Bolin C., Perolat P. Leptospira and Leptospirosis. 2nd ed. MediSci; Melbourne, VIC, Australia: 1999.
-
- Torgerson P.R., Hagan J.E., Costa F., Calcagno J., Kane M., Martinez-Silveira M.S., Goris M.G., Stein C., Ko A.I., Abela-Ridder B. Global burden of leptospirosis: Estimated in terms of disability adjusted life years. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015;9:e0004122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

