Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study
- PMID: 32429077
- PMCID: PMC7284598
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12051429
Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study
Abstract
Background and aims: Clinical evidence for the benefits of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) is lacking in advanced liver disease. We evaluated the potential benefits of long-term oral BCAA supplementation in patients with advanced liver disease.
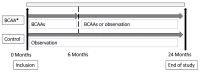
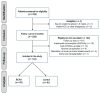
Methods: Liver cirrhosis patients with Child-Pugh (CP) scores from 8 to 10 were prospectively recruited from 13 medical centers. Patients supplemented with 12.45 g of daily BCAA granules over 6 months, and patients consuming a regular diet were assigned to the BCAA and control groups, respectively. The effects of BCAA supplementation were evaluated using the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score, CP score, serum albumin, serum bilirubin, incidence of cirrhosis-related events, and event-free survival for 24 months.
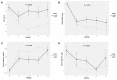
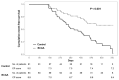
Results: A total of 124 patients was analyzed: 63 in the BCAA group and 61 in the control group. The MELD score (p = 0.009) and CP score (p = 0.011) significantly improved in the BCAA group compared to the control group over time. However, the levels of serum albumin and bilirubin in the BCAA group did not improve during the study period. The cumulative event-free survival was significantly improved in the BCAA group compared to the control group (HR = 0.389, 95% CI = 0.221-0.684, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Long-term supplementation with oral BCAAs can potentially improve liver function and reduce major complications of cirrhosis in patients with advanced liver disease.
Keywords: amino acids; ascites; branched-chain; hepatic encephalopathy; liver cirrhosis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest about this work.
Figures
References
-
- Marchesini G., Bianchi G., Merli M., Amodio P., Panella C., Loguercio C., Rossi Fanelli F., Abbiati R., Italian B.S.G. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: A double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1792–1801. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00323-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

