The use of information and communication technologies in Latin American dentists: a cross-sectional study from Ecuador
- PMID: 32429887
- PMCID: PMC7236194
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-020-01137-z
The use of information and communication technologies in Latin American dentists: a cross-sectional study from Ecuador
Abstract
Background: The use of information and communication technologies (ICTs) provide the tools for enabling fast and reliable real-time communications, as well as the transfer of information between dental professionals and their patients. However, little is known about the frequency and preference of ICTs among Latin-American dentists. Our study aims to fill this gap by assessing different aspects related to ICTs, mainly the frequency of use, perceptions, and barriers among Ecuadorian dentists.
Methods: An anonymous, cross-sectional survey-based study was conducted among 342 Ecuadorian dentists. The final questionnaire included 13 items related to the frequency of use, perceptions, and barriers of ICTs. Bivariate analysis was performed by using chi-squared testing to explore the association between the independent variables and the intended use of ICTs, as well as to characterize the perceptions and barriers related to ICTs.
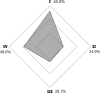
Results: In general, most participants reported the use of ICTs to communicate with colleagues (99.7%), and patients (96.2%), while only 63.5% reported using ICTs to obtain academic information in their daily practice. WhatsApp was rated as the most used ICT for communicating with colleagues and patients. A majority of participants considered that ICTs can be useful for facilitating continuing dental education (92.1%), searching new work opportunities (91.5%), promoting health (90.1%), working with colleagues and other health professionals (91.2%), promoting their professional services (90.6%), and for resolving clinical cases (87.7%). On the subject of barriers, privacy and security concerns about personal and/or patient information was the biggest concern among dentists (65%), followed by lack of time to learn how to use and/or use ICTs (48%), lack of mobile internet access (28.1%), and lack of internet access at work (24.9%).
Conclusion: In our study, we found that Ecuadorian dentists had a high usage rate of ICTs, mainly for communicating with other colleagues and patients, while the academic use of technology remains a comparatively underused application. Most of the participants surveyed had a positive perception towards ICTs, while privacy and security concerns were identified as the main barrier. Older age was associated with a less favourable perception toward ICTs, as well as an increased likelihood of reporting barriers related to the use of technology.
Keywords: Dentists; Ecuador; Information and communication technologies; Latin America; Social media.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ecuadorian Cancer Patients' Preference for Information and Communication Technologies: Cross-Sectional Study.J Med Internet Res. 2018 Feb 20;20(2):e50. doi: 10.2196/jmir.8485. J Med Internet Res. 2018. PMID: 29463492 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of Use, Perceptions and Barriers of Information and Communication Technologies Among Latin American Physicians: An Ecuadorian Cross-Sectional Study.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020 Mar 12;13:259-269. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S246253. eCollection 2020. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020. PMID: 32214821 Free PMC article.
-
Use and preferences of information and communication technologies in patients with hypertension: a cross-sectional study in Ecuador.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2019 Jul 24;12:583-590. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S208861. eCollection 2019. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2019. PMID: 31413585 Free PMC article.
-
Information and communication technology-based interventions for chronic diseases consultation: Scoping review.Int J Med Inform. 2022 Jul;163:104784. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2022.104784. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Int J Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 35525127
-
The Use of Information and Communication Technologies by Sex Workers to Manage Occupational Health and Safety: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Jun 24;23(6):e26085. doi: 10.2196/26085. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34185001 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Technological and Socio-Demographic Factors Influencing Telemedicine Literacy in Trinidad and Tobago: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Multidimensional Approach.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 20;8(2):e70420. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70420. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39980826 Free PMC article.
-
The use of social media for professional purposes among dentists in Saudi Arabia.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Jan 12;21(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01390-w. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 33435911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Catan G, Espanha R, Mendes R, Toren O, Chinitz D. The Impact of eHealth and mHealth on doctor behavior and patient involvement: an Israeli and Portuguese comparative approach. Impact eHealth mHealth Doctor Behav Patient Invol. 2015:813–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

