Zebrafish models of skeletal dysplasia induced by cholesterol biosynthesis deficiency
- PMID: 32430393
- PMCID: PMC7328163
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.042549
Zebrafish models of skeletal dysplasia induced by cholesterol biosynthesis deficiency
Abstract
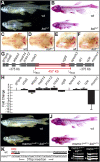
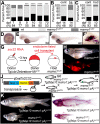
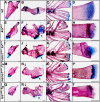
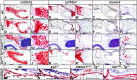
Human disorders of the post-squalene cholesterol biosynthesis pathway frequently result in skeletal abnormalities, yet our understanding of the mechanisms involved is limited. In a forward-genetic approach, we have found that a late-onset skeletal mutant, named kolibernu7 , is the result of a cis-acting regulatory mutation leading to loss of methylsterol monooxygenase 1 (msmo1) expression within pre-hypertrophic chondrocytes. Generated msmo1nu81 knockdown mutation resulted in lethality at larval stage. We demonstrated that this is a result of both cholesterol deprivation and sterol intermediate accumulation by creating a mutation eliminating activity of Lanosterol synthase (Lss). Our results indicate that double lssnu60;msmo1nu81 and single lssnu60 mutants survive significantly longer than msmo1nu81 homozygotes. Liver-specific restoration of either Msmo1 or Lss in corresponding mutant backgrounds suppresses larval lethality. Rescued mutants develop dramatic skeletal abnormalities, with a loss of Msmo1 activity resulting in a more-severe patterning defect of a near-complete loss of hypertrophic chondrocytes marked by col10a1a expression. Our analysis suggests that hypertrophic chondrocytes depend on endogenous cholesterol synthesis, and blocking C4 demethylation exacerbates the cholesterol deficiency phenotype. Our findings offer new insight into the genetic control of bone development and provide new zebrafish models for human disorders of the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Chondrodysplasia punctata; Lss; Msmo1; Skeletal dysplasia; Zebrafish.
© 2020. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Avaron F., Hoffman L., Guay D. and Akimenko M. A. (2006). Characterization of two new zebrafish members of the hedgehog family: atypical expression of a zebrafish indian hedgehog gene in skeletal elements of both endochondral and dermal origins. Dev. Dyn. 235, 478-489. 10.1002/dvdy.20619 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Besnard T., Sloboda N., Goldenberg A., Kury S., Cogne B., Breheret F., Trochu E., Conrad S., Vincent M., Deb W. et al. (2019). Biallelic pathogenic variants in the lanosterol synthase gene LSS involved in the cholesterol biosynthesis cause alopecia with intellectual disability, a rare recessive neuroectodermal syndrome. Genet. Med. 21, 2025 10.1038/s41436-019-0445-x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

