Efficient flow synthesis of human antimicrobial peptides
- PMID: 32431323
- PMCID: PMC7236790
- DOI: 10.1071/CH20043
Efficient flow synthesis of human antimicrobial peptides
Abstract
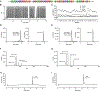
Organisms from all kingdoms of life have evolved a vast array of peptidic natural products to defend against microbes. These are known collectively as antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) or host defense peptides, reflecting their abilities to not only directly kill microbes, but also to modulate host immune responses. Despite decades of investigation, AMPs have yet to live up to their promise as lead therapeutics, a reality that reflects, in part, our incomplete understanding of these diverse agents in their various physiological contexts. Toward improving our understanding of AMP biology and the ways in which this can be best leveraged for therapeutic development, we are interested in large-scale comparisons of the antimicrobial and immunological activities of human AMPs, an undertaking that requires an efficient workflow for AMP synthesis and subsequent characterization. We describe here the application of flow chemistry and reverse phase flash chromatography to the generation of 43 AMPs, approaches that, when combined, significantly expedite synthesis and purification, potentially facilitating more systematic approaches to downstream testing and engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST JSA declares no conflicts of interest. BLP is a founder of Amide Technologies and Resolute Bio.
Figures

References
-
- Eisenstein BI, Oleson FB Jr, Baltz RH. Daptomycin: From the Mountain to the Clinic, with Essential Help from Francis Tally, MD. Clin Infect Dis [Internet]. 2010. January [cited 2020 Jan 20];50(s1):S10–5. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-lookup/doi/10.1086/647938 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luther A, Urfer M, Zahn M, Müller M, Wang SY, Mondal M, et al. Chimeric peptidomimetic antibiotics against Gram-negative bacteria. Nature. 2019. December 19; - PubMed
-
- Srinivas N, Jetter P, Ueberbacher BJ, Werneburg M, Zerbe K, Steinmann J, et al. Peptidomimetic antibiotics target outer-membrane biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Science [Internet]. 2010. February 19 [cited 2018 Aug 30];327(5968):1010–3. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20167788 - PubMed
-
- Mourtada R, Herce HD, Yin DJ, Moroco JA, Wales TE, Engen JR, et al. Design of stapled antimicrobial peptides that are stable, nontoxic and kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria in mice. Nat Biotechnol [Internet]. 2019. October 19 [cited 2019 Oct 4];37(10):1186–97. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31427820 - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
