Astaxanthin Attenuates Neuroinflammation in Status Epilepticus Rats by Regulating the ATP-P2X7R Signal
- PMID: 32431490
- PMCID: PMC7201036
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S249162
Astaxanthin Attenuates Neuroinflammation in Status Epilepticus Rats by Regulating the ATP-P2X7R Signal
Abstract
Background: As a life-threatening neurological emergency, status epilepticus (SE) is often refractory to available treatment. Current studies have shown a causal role of neuroinflammation in patients with lower seizure thresholds and driving seizures. The ATP-gated purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is mainly expressed on the microglia, which function as gatekeepers of inflammation. Although emerging evidence has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects of astaxanthin (AST) in SE, the associated mechanism remains unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to clarify the effects of AST on P2X7R-related inflammation in SE.
Methods: SE was induced in rats using lithium-pilocarpine, and AST was administered 1 h after SE induction. Rat microglia were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), AST, ATP, 2,3-O-4-benzoyl-4-benzoyl-ATP (BzATP) and oxidized ATP (oxATP). The Morris water maze, immunohistochemistry, and Nissl staining were performed in rats. Expressions of P2X7R and inflammatory cytokines (such as cycloxygenase-2 (Cox-2), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)) were detected using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot (WB) both in rats and microglia. ATP concentration in the microglia was evaluated using ELISA.
Results: The AST alleviated hippocampal injury and improved cognitive dysfunction induced by SE. AST also effectively inhibited inflammation and downregulated P2X7R expression in both rat brain and microglia. The results also showed that AST reduced the extracellular ATP levels and that P2X7R expression could be increased by extracellular ATP. In addition, BzATP upregulates the expression of P2X7R and inflammatory factors in microglia. Conversely, it downregulates the expression of P2X7R and inflammatory factors.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that AST attenuated ATP-P2X7R mediated inflammation in SE.
Keywords: ATP; P2X7R; astaxanthin; neuroinflammation; status epilepticus.
© 2020 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

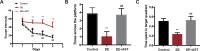





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

