Efficacy and safety of aerosol inhalation of recombinant human interferon α1b (IFNα1b) injection for noninfluenza viral pneumonia, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 32431566
- PMCID: PMC7221328
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-020-00249-1
Efficacy and safety of aerosol inhalation of recombinant human interferon α1b (IFNα1b) injection for noninfluenza viral pneumonia, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: To investigate the efficacy and safety of aerosol inhalation of recombinant human interferon α1b (IFNα1b) injection for noninfluenza viral pneumonia.
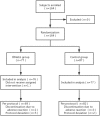
Methods: One hundred sixty-four patients with noninfluenza viral pneumonia were divided into IFNα1b and control groups. The IFNα1b group received routine treatment + aerosol inhalation of recombinant human IFNα1b injection (50 μg × 2 injections, bid). The control group received routine treatment + IFN analog (two injections, bid). Overall response rate (ORR) of five kinds clinical symptoms. Further outcomes were daily average score and the response rate of each of the symptoms above.
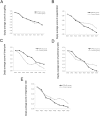
Results: A total of 163 patients were included in the full analysis set (FAS) and 151 patients were included in the per-protocol set (PPS). After 7 days of treatment, ORR of clinical symptoms was higher in IFNα1b group than that in control group for both the FAS and PPS. Moreover, after 7 days of treatment, the daily score of three efficacy indexes including expectoration, respiratory rate, and pulmonary rales were improved. The ORRs for expectoration and pulmonary rales were higher in the IFNα1b group than in the control group (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences of the ORRs for coughing, chest pain and respiratory rate between the two groups (P > 0.05). The incidence of adverse events was 6.5% (n = 5) in IFNα1b group and 3.5% (n = 3) in control group (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Aerosol inhalation of recombinant human IFNα1b is safe and it can improve the clinical symptoms of noninfluenza viral pneumonia.
Keywords: Aerosol inhalation; Clinical trial; Noninfluenza viral pneumonia; Recombinant human interferon α1b.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GB05, a safe and effective IFNα1b inhalation solution for treating respiratory syncytial virus infection.Int J Pharm. 2025 Mar 30;673:125426. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125426. Epub 2025 Mar 2. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40037489
-
Efficacy and safety of Lianhua Qingwen granule in the treatment of non-influenza viral pneumonia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 17;10:1302219. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1302219. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38314028 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Inhaling Different Dosage Recombinant Human Interferon α1B for Bronchiolitis in Children: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 27;2022:2229735. doi: 10.1155/2022/2229735. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35529920 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of interferon on neonates with respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Dec;20(6):220. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9350. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 33193835 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, controlled, multicenter clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral sitafloxacin versus moxifloxacin in adult patients with community-acquired pneumonia.Curr Med Res Opin. 2021 Apr;37(4):693-701. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2021.1885362. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021. PMID: 33534617 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Type I interferon: From innate response to treatment for COVID-19.Pediatr Investig. 2020 Dec 28;4(4):275-280. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12226. eCollection 2020 Dec. Pediatr Investig. 2020. PMID: 33376955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduning injection combined with western medicine for pneumonia: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22757. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022757. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120780 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Nebulized GB05-Human IFNα1b Inhalation Solution: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Escalation Phase I Study in Healthy Chinese Adult Volunteers.Infect Dis Ther. 2024 Sep;13(9):2053-2070. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-01024-y. Epub 2024 Aug 4. Infect Dis Ther. 2024. PMID: 39097549 Free PMC article.
-
The safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of nebulized pegylated interferon α-2b in healthy adults: a randomized phase 1 trial.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 May 12;26(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00937-9. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40355915 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interferon-based agents for current and future viral respiratory infections: A scoping literature review of human studies.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022 Apr 6;2(4):e0000231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000231. eCollection 2022. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36962150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J, Tejada-Vera B. Deaths: final data for 2014. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2016;65:1–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous