Structures Illuminate Cardiac Ion Channel Functions in Health and in Long QT Syndrome
- PMID: 32431610
- PMCID: PMC7212895
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00550
Structures Illuminate Cardiac Ion Channel Functions in Health and in Long QT Syndrome
Abstract
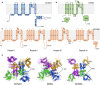
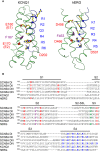
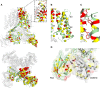
The cardiac action potential is critical to the production of a synchronized heartbeat. This electrical impulse is governed by the intricate activity of cardiac ion channels, among them the cardiac voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels KCNQ1 and hERG as well as the voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel encoded by SCN5A. Each channel performs a highly distinct function, despite sharing a common topology and structural components. These three channels are also the primary proteins mutated in congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS), a genetic condition that predisposes to cardiac arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death due to impaired repolarization of the action potential and has a particular proclivity for reentrant ventricular arrhythmias. Recent cryo-electron microscopy structures of human KCNQ1 and hERG, along with the rat homolog of SCN5A and other mammalian sodium channels, provide atomic-level insight into the structure and function of these proteins that advance our understanding of their distinct functions in the cardiac action potential, as well as the molecular basis of LQTS. In this review, the gating, regulation, LQTS mechanisms, and pharmacological properties of KCNQ1, hERG, and SCN5A are discussed in light of these recent structural findings.
Keywords: KCNQ1; SCN5A; cardiac action potential; hERG; long QT syndrome; structural biology.
Copyright © 2020 Brewer, Kuenze, Vanoye, George, Meiler and Sanders.
Figures






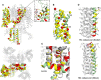
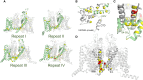
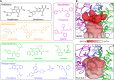
References
-
- Abbott G. W. (2014). Biology of the KCNQ1 Potassium Channel. New J. Sci. 2014, 26. 10.1155/2014/237431 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

