Clinical and Electroencephalographic Features of the Seizures in Neuronal Surface Antibody-Associated Autoimmune Encephalitis
- PMID: 32431657
- PMCID: PMC7214674
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00280
Clinical and Electroencephalographic Features of the Seizures in Neuronal Surface Antibody-Associated Autoimmune Encephalitis
Abstract
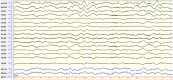
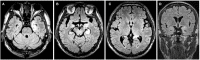
Objectives: To investigate clinical and electroencephalographic features of the seizures in different types of neuronal surface antibody (NSAb)-associated autoimmune encephalitis (AE). Methods: The clinical data of the seizures were analyzed in 18 patients with NSAb-associated AEs diagnosed in the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. Results: From May 2013 to April 2019, a total of 18 cases of NSAb-associated AE were diagnosed, including 9 cases of leucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 protein (LGI1) antibody-associated encephalitis, 7 cases of anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis, and 2 cases of anti-γ-aminobutyric acid B receptor (GABABR) encephalitis. All nine cases (100%) with LGI1 AE had seizures manifesting in three types: faciobranchial dystonia seizure (FBDS) (44.4%), mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE)-like seizure (66.7%), and focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizure (FBTCS) (77.8%). Six of nine (66.7%) showed abnormal signal on hippocampus or basal ganglia in brain MRI. Five of seven cases (71%) with anti-NMDAR encephalitis had seizures manifesting in three types: focal aware seizure (40%), focal-impaired awareness seizure (20%), generalized tonic-clonic seizure (GTCS) (100%), and status epilepticus (SE) (40%). Three of seven (42.8%) showed abnormalities in brain MRI. Both patients with anti-GABABR encephalitis had seizures manifesting in two types: GTCS and MTLE-like seizure, one with SE. One showed abnormal signal on left hippocampus in brain MRI. All patients (100%) with three types of AE had abnormalities in electroencephalogram (EEG), showing diffuse (4/18) or focal slow waves (14/18) in background, interictal (10/18), or ictal (6/18) epileptic discharges in the temporal or other regions; two patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis showed delta activity or rhythm in frontotemporal region. All patients with seizures showed good response to immunotherapy except one with LGI1 AE. Conclusions: Most patients with NSAb-associated AE had seizures; seizure types varied between different types of AE. In LGI1 AE, the hippocampus and basal ganglia were two main targets; the corresponding seizure type was MTLE-like seizure and FBDS, respectively. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis had more generalized than focal seizures. Delta activity or rhythm in the frontotemporal region in EEG was helpful for diagnosis. Anti-GABABR encephalitis was characterized by refractory seizures as initial symptom, mainly GTCS or MTLE-like seizure. Most seizures in NSAb-associated AE showed good response to immunotherapy, and antiepileptic drugs should be considered as an add-on symptomatic treatment.
Keywords: GABABR antibody; LGI1 antibody; NMDAR antibody; autoimmune encephalitis; neuronal surface antibody; seizure.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Yu, Hu, Li, Song and Wang.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical features of nine cases of leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 protein antibody-associated encephalitis.Acta Neurol Belg. 2021 Aug;121(4):889-897. doi: 10.1007/s13760-020-01336-z. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Acta Neurol Belg. 2021. PMID: 32232701
-
Electroencephalographic biomarkers of antibody-mediated autoimmune encephalitis.Front Neurol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1510722. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1510722. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40206289 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and long-term outcomes of seizures associated with autoimmune encephalitis: A follow-up study in East China.J Clin Neurosci. 2019 Oct;68:73-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.07.049. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31331752
-
Seizures in autoimmune encephalitis: specific features based on a systematic comparative study.Epileptic Disord. 2021 Dec 1;23(6):879-892. doi: 10.1684/epd.2021.1355. Epileptic Disord. 2021. PMID: 34704941
-
Electroencephalographic findings in antileucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 (LGI1) autoimmune encephalitis: A systematic review.Epilepsy Behav. 2020 Nov;112:107462. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107462. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Epilepsy Behav. 2020. PMID: 32971385
Cited by
-
Factors Influencing the Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs in Adult Patients with Symptomatic Seizures Secondary to Neuronal Surface Antibodies-Associated Autoimmune Encephalitis.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 9;15:927-937. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S347893. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35173460 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Pediatric anti-gamma aminobutyric acid-B receptor encephalitis with benign prognosis.Front Pediatr. 2023 Mar 3;11:1104001. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1104001. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36937947 Free PMC article.
-
Movement disorders in autoimmune encephalitis: an update.J Neurol. 2023 Nov;270(11):5288-5302. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11881-1. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37523063 Review.
-
FLAMES overlaying anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: a case report and literature review.BMC Neurol. 2024 Apr 25;24(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03617-z. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38664672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Reasoning: A Young Adult With New Seizures and Chapeau de Gendarme.Neurology. 2023 Oct 31;101(18):e1821-e1827. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207827. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Neurology. 2023. PMID: 37580161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Association N b.o.t.C.M. Chinese experts consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune encephalitis. Chin J Neurol. (2017) 50:91–8. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2017.02.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

