Lipin-1 Contributes to IL-4 Mediated Macrophage Polarization
- PMID: 32431707
- PMCID: PMC7214697
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00787
Lipin-1 Contributes to IL-4 Mediated Macrophage Polarization
Abstract
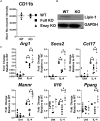
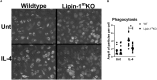
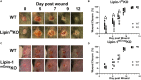
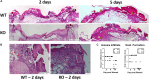
Macrophage responses contribute to a diverse array of pathologies ranging from infectious disease to sterile inflammation. Polarization of macrophages determines their cellular function within biological processes. Lipin-1 is a phosphatidic acid phosphatase in which its enzymatic activity contributes to macrophage pro-inflammatory responses. Lipin-1 also possesses transcriptional co-regulator activity and whether this activity is required for macrophage polarization is unknown. Using mice that lack only lipin-1 enzymatic activity or both enzymatic and transcriptional coregulator activities from myeloid cells, we investigated the contribution of lipin-1 transcriptional co-regulator function toward macrophage wound healing polarization. Macrophages lacking both lipin-1 activities did not elicit IL-4 mediated gene expression to levels seen in either wild-type or lipin-1 enzymatically deficient macrophages. Furthermore, mice lacking myeloid-associated lipin-1 have impaired full thickness excisional wound healing compared to wild-type mice or mice only lacking lipin-1 enzymatic activity from myeloid cell. Our study provides evidence that lipin-1 transcriptional co-regulatory activity contributes to macrophage polarization and influences wound healing in vivo.
Keywords: lipin-1; macrophage; polarization; transcriptional coregulator; wound healing.
Copyright © 2020 Chandran, Schilke, Blackburn, Yurochko, Mirza, Scott, Finck and Woolard.
Figures


References
-
- Jennewein C, Kuhn AM, Schmidt MV, Meilladec-Jullig V, von Knethen A, Gonzalez FJ, et al. Sumoylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma by apoptotic cells prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced NCoR removal from kappaB binding sites mediating transrepression of proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol. (2008) 181:5646–52. 10.4049/jimmunol.181.8.5646 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

