Patterns of C1-Inhibitor/Plasma Serine Protease Complexes in Healthy Humans and in Hereditary Angioedema Patients
- PMID: 32431708
- PMCID: PMC7214733
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00794
Patterns of C1-Inhibitor/Plasma Serine Protease Complexes in Healthy Humans and in Hereditary Angioedema Patients
Abstract
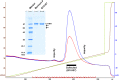
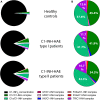
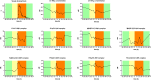
C1-inhibitor (C1-INH) is an important regulator of the complement, coagulation, fibrinolytic and contact systems. The quantity of protease/C1-INH complexes in the blood is proportional to the level of the in vivo activation of these four cascade-like plasma enzyme systems. Parallel determination of C1-INH-containing activation complexes could be important to understand the regulatory role of C1-INH in diseases such as hereditary angioedema (HAE) due to C1-INH deficiency (C1-INH-HAE). We developed in-house ELISAs to measure the concentration of complexes of C1-INH formed with active proteases: C1r, C1s, MASP-1, MASP-2, plasma kallikrein, factor XIIa, factor XIa, and thrombin, as well as to determine total and functionally active C1-INH. We measured the concentration of the complexes in EDTA plasma from 6 healthy controls, from 5 with type I and 5 with type II C1-INH-HAE patients during symptom-free periods and from five patients during HAE attacks. We also assessed the concentration of these complexes in blood samples taken from one C1-INH-HAE patient during the kinetic follow-up of a HAE attack. The overall pattern of complexed C1-INH was similar in controls and C1-INH-HAE patients. C1-INH formed the highest concentration complexes with C1r and C1s. We observed higher plasma kallikrein/C1-INH complex concentration in both type I and type II C1-INH-HAE, and higher concentration of MASP-1/C1-INH, and MASP-2/C1-INH complexes in type II C1-INH-HAE patients compared to healthy controls and type I patients. Interestingly, none of the C1-INH complex concentrations changed significantly during HAE attacks. During the kinetic follow-up of an HAE attack, the concentration of plasma kallikrein/C1-INH complex was elevated at the onset of the attack. In parallel, C1r, FXIIa and FXIa complexes of C1-INH also tended to be elevated, and the changes in the concentrations of the complexes followed rather rapid kinetics. Our results suggest that the complement classical pathway plays a critical role in the metabolism of C1-INH, however, in C1-INH-HAE, contact system activation is the most significant in this respect. Due to the fast changes in the concentration of complexes, high resolution kinetic follow-up studies are needed to clarify the precise molecular background of C1-INH-HAE pathogenesis.
Keywords: C1-inhibitor; HAE attack; activation; hereditary angioedema; kinetic follow-up; serine protease.
Copyright © 2020 Kajdácsi, Jandrasics, Veszeli, Makó, Koncz, Gulyás, Köhalmi, Temesszentandrási, Cervenak, Gál, Dobó, de Maat, Maas, Farkas and Varga.
Figures

References
-
- Gregorek H, Kokai M, Hidvegi T, Fust G, Sabbouh K, Madalinski K. Concentration of C1 inhibitor in sera of healthy blood donors as studied by immunoenzymatic assay. Compl Inflamm. (1991) 8:310–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

