A Pauci-Immune Synovial Pathotype Predicts Inadequate Response to TNFα-Blockade in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 32431716
- PMCID: PMC7214807
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00845
A Pauci-Immune Synovial Pathotype Predicts Inadequate Response to TNFα-Blockade in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
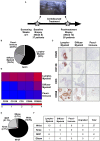
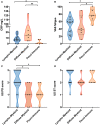
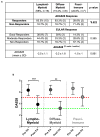
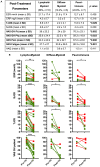
Objectives: To assess whether the histopathological features of the synovium before starting treatment with the TNFi certolizumab-pegol could predict clinical outcome and examine the modulation of histopathology by treatment. Methods: Thirty-seven RA patients fulfilling UK NICE guidelines for biologic therapy were enrolled at Barts Health NHS trust and underwent synovial sampling of an actively inflamed joint using ultrasound-guided needle biopsy before commencing certolizumab-pegol and after 12-weeks. At 12-weeks, patients were categorized as responders if they had a DAS28 fall >1.2. A minimum of 6 samples was collected for histological analysis. Based on H&E and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for CD3 (T cells), CD20 (B cells), CD138 (plasma cells), and CD68 (macrophages) patients were categorized into three distinct synovial pathotypes (lympho-myeloid, diffuse-myeloid, and pauci-immune). Results: At baseline, as per inclusion criteria, DAS28 mean was 6.4 ± 0.9. 94.6% of the synovial tissue was retrieved from the wrist or a metacarpophalangeal joint. Histological pathotypes were distributed as follows: 58% lympho-myeloid, 19.4% diffuse-myeloid, and 22.6% pauci-immune. Patients with a pauci-immune pathotype had lower levels of CRP but higher VAS fatigue compared to lympho- and diffuse-myeloid. Based on DAS28 fall >1.2, 67.6% of patients were deemed as responders and 32.4% as non-responders. However, by categorizing patients according to the baseline synovial pathotype, we demonstrated that a significantly higher number of patients with a lympho-myeloid and diffuse-myeloid pathotype in comparison with pauci-immune pathotype [83.3% (15/18), 83.3 % (5/6) vs. 28.6% (2/7), p = 0.022) achieved clinical response to certolizumab-pegol. Furthermore, we observed a significantly higher level of post-treatment tender joint count and VAS scores for pain, fatigue and global health in pauci-immune in comparison with lympho- and diffuse-myeloid patients but no differences in the number of swollen joints, ESR and CRP. Finally, we confirmed a significant fall in the number of CD68+ sublining macrophages post-treatment in responders and a correlation between the reduction in the CD20+ B-cells score and the improvement in the DAS28 at 12-weeks. Conclusions: The analysis of the synovial histopathology may be a helpful tool to identify among clinically indistinguishable patients those with lower probability of response to TNFα-blockade.
Keywords: anti-TNF; certolizumab-pegol; pathotype; rheumatoid arthritis; synovial tissue.
Copyright © 2020 Nerviani, Di Cicco, Mahto, Lliso-Ribera, Rivellese, Thorborn, Hands, Bellan, Mauro, Boutet, Giorli, Lewis, Kelly, Bombardieri, Humby and Pitzalis.
Figures
References
-
- Salliot C, Finckh A, Katchamart W, Lu Y, Sun Y, Bombardier C, et al. Indirect comparisons of the efficacy of biological antirheumatic agents in rheumatoid arthritis in patients with an inadequate response to conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or to an anti-tumour necrosis factor agent: a meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2011) 70:266–71. 10.1136/ard.2010.132134 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Machold KP, Stamm TA, Nell VPK, Pflugbeil S, Aletaha D, Steiner G, et al. Very recent onset rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and serological patient characteristics associated with radiographic progression over the first years of disease. Rheumatology. (2007) 46:342–9. 10.1093/rheumatology/kel237 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

