Therapeutic strategies for ischemia reperfusion injury in emergency medicine
- PMID: 32431842
- PMCID: PMC7231568
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.501
Therapeutic strategies for ischemia reperfusion injury in emergency medicine
Abstract
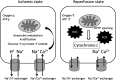
Ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury occurs when blood supply, perfusion, and concomitant reoxygenation is restored to an organ or area following an initial poor blood supply after a critical time period. Ischemia reperfusion injury contributes to mortality and morbidity in many pathological conditions in emergency medicine clinical practice, including trauma, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, and post-cardiac arrest syndrome. The process of IR is multifactorial, and its pathogenesis involves several mechanisms. Reactive oxygen species are considered key molecules in reperfusion injury due to their potent oxidizing and reducing effects that directly damage cellular membranes by lipid peroxidation. In general, IR injury to an individual organ causes various pro-inflammatory mediators to be released, which could then induce inflammation in remote organs, thereby possibly advancing the dysfunction of multiple organs. In this review, we summarize IR injury in emergency medicine. Potential therapies include pharmacological treatment, ischemic preconditioning, and the use of medical gases or vitamin therapy, which could significantly help experts develop strategies to inhibit IR injury.
Keywords: Emergency medicine; inflammation; ischemia reperfusion; remote ischemic preconditioning; shock; therapeutic hypothermia.
© 2020 The Authors. Acute Medicine & Surgery published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Association for Acute Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Approval of the research protocol: N/A. Informed consent: N/A. Registry and registration no. of the study/trial: N/A. Animal studies: N/A. Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

