VEGF Production Is Regulated by the AKT/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway and Controls the Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii in ARPE-19 Cells
- PMID: 32432052
- PMCID: PMC7216739
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00184
VEGF Production Is Regulated by the AKT/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway and Controls the Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii in ARPE-19 Cells
Abstract
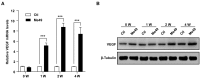
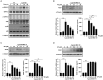
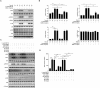
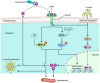
The retina is the primary site of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the eye, and choroidal neovascularization in ocular toxoplasmosis is one of the most important causes of visual impairment. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the key regulators of blood vessel development, however, little is known about the mechanisms of T. gondii-induced VEGF production in ocular toxoplasmosis. Here, we investigate the effect of T. gondii on VEGF production regulation in human retinal pigment epithelium ARPE-19 cells and attempted to unveil the underlying mechanism of this event by focusing on the interaction between parasite and the selected host intracellular signaling pathways. T. gondii infection increased the expression of VEGF mRNA and protein in ARPE-19 cells in parasite burden- and infection time-dependent manner. The proportional increase of VEGF upstream regulators, HIF-1α and HO-1, was also observed. T. gondii induced the activation of host p-AKT, p-ERK1/2, and p-p38 MAPK in ARPE-19 cells in a parasite-burden dependent manner. However, VEGF expression decreased after the pre-treatment with PI3K inhibitors (LY294002 and GDC-0941), ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD098059), and p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580), but not JNK inhibitor (SP600125), in a dose-dependent manner. The anti-VEGF agent bevacizumab or VEGF siRNA transfection prominently inhibited the activation of p-AKT and p-ERK1/2, but not p-p38 MAPK and JNK1/2 in T. gondii-infected ARPE-19 cells. Bevacizumab treatment or VEGF siRNA transfection significantly inhibited the proliferation of T. gondii tachyzoites in the host cell, dose-dependently, but not invasion of parasites. VEGF-receptor 2 (VEGF-R2) antagonist, SU5416, attenuated VEGF production and tachyzoite proliferation in T. gondii-infected ARPE-19 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Collectively, T. gondii prominently induces VEGF production in ARPE-19 cells, and VEGF and AKT/ERK1/2 signaling pathways mutually regulate each other in T. gondii-infected ARPE-19 cells, but not p38 MAPK and JNK1/2 signaling pathways. VEGF and VEGF-R2 control the parasite proliferation in T. gondii-infected ARPE-19 cells. From this study, we revealed the putative mechanisms for VEGF induction as well as the existence of positive feedback between VEGF and PI3K/MAPK signaling pathways in T. gondii-infected retinal pigment epithelium.
Keywords: PI3K/MAPK signaling pathways; Toxoplasma gondii proliferation; ocular toxoplasmosis; retinal pigment epithelium; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Copyright © 2020 Quan, Ismail, Cha, Jo, Gao, Choi, Chu, Yuk and Lee.
Figures






References
-
- Bussolati B., Mason J. C. (2006). Dual role of VEGF-induced heme-oxygenase-1 in ANGIOGENESIS. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8, 1153–1163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

