Endotracheal Surfactant Combined With Budesonide for Neonatal ARDS
- PMID: 32432062
- PMCID: PMC7214613
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.00210
Endotracheal Surfactant Combined With Budesonide for Neonatal ARDS
Abstract
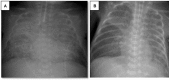
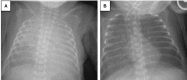
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a clinical condition characterized by acute diffuse inflammatory lung injury and severe hypoxemia. In 2017, the Montreux Consensus defined diagnostic criteria for ARDS in the neonatal period. The management of ARDS includes strict adherence to lung-protective ventilation strategies and therapeutic agents to improve gas exchange. We report two similar cases of premature infants with gestational ages of 23 and 24 weeks diagnosed with neonatal ARDS according to the Montreux definition. These patients developed acute worsening of oxygenation on the 30th and 28th day of life, respectively, while they were ventilated on volume-guarantee assist/control mode. Chest X-rays revealed bilateral diffuse opacity, there were no cardiogenic origins for pulmonary edema, and their oxygenation indexes were >8. Both cases fulfilled the neonatal ARDS criteria and the patients' clinical conditions were associated with late onset neonatal sepsis. After lung recruitment maneuver, the infants began HFO volume-guarantee ventilation and received surfactant treatment. Since they showed a poor short-term response, intratracheal surfactant of 100 mg/kg plus budesonide of 0.25 mg/kg were administered and their oxygenation indexes were reduced stepwise. Both patients survived and were discharged home with spontaneous breathing of room air. Neonatal ARDS is generally an underdiagnosed condition associated with sepsis, pneumonia, and meconium aspiration. Impaired surfactant activity and reduced lung compliance play important roles in its pathophysiology. To our knowledge, this is the first case report indicating the possible therapeutic role of budesonide plus surfactant in ARDS treatment. Since ARDS is an entity not recognized in newborns, we want to emphasize neonatal ARDS diagnosis and underline that the combination of budesonide and surfactant may be a novel therapeutic option in the treatment of ARDS.
Keywords: ELGAN Extremely low gestational age newborn; Montreux criteria; neonatal ARDS; surfactant; surfactant plus budesonid.
Copyright © 2020 Deliloglu, Tuzun, Cengiz, Ozkan and Duman.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endotracheal Surfactant and Budesonide Combination Therapy in Neonatal Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome due to Late-Onset Sepsis.Arch Iran Med. 2024 Oct 1;27(10):573-579. doi: 10.34172/aim.31725. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Arch Iran Med. 2024. PMID: 39492564 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Montreux definition with the Berlin definition for neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Apr;182(4):1673-1684. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-04848-x. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36735062
-
The role of surfactant treatment in preterm infants and term newborns with acute respiratory distress syndrome.J Perinatol. 2009 May;29 Suppl 2:S18-22. doi: 10.1038/jp.2009.30. J Perinatol. 2009. PMID: 19399004 Review.
-
Inhalation or instillation of steroids for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Neonatology. 2015;107(4):358-9. doi: 10.1159/000381132. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Neonatology. 2015. PMID: 26044104 Review.
-
The perinatal period should be considered in neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome: comparison of the Montreux definition vs. the second pediatric acute lung injury consensus conference definition.Front Pediatr. 2023 Sep 28;11:1216073. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1216073. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37842021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of the efficacy of budesonide and ambroxol hydrochloride inhalation in children with pneumonia and their effects on inflammatory response.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 19;9(11):e21105. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21105. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37954384 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant therapies for pediatric and neonatal ARDS: ESPNIC expert consensus opinion for future research steps.Crit Care. 2021 Feb 22;25(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03489-6. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33618742 Free PMC article.
-
Low Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) Level is Associated with an Increased Risk of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Preterm Infants with Different Gestational Ages: A Retrospective Study.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Nov 12;17:5219-5231. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S486224. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39554870 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamic and Structural Study of Budesonide-Exogenous Lung Surfactant System.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 4;25(5):2990. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052990. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474237 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to protect surfactant and enhance its activity.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6):654-662. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.07.011. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34365021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Venkataraman R, Kamaluddeen M, Hasan SU, Robertson HL, Lodha A. Intratracheal administration of budesonide-surfactant in prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very low birth weight infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatric Pulmonol. (2017) 52:968–75. - PubMed
-
- Bem RA. Neonatal ARDS: it's about time we take it to the next level. J Emerg Critical Care Med. (2017) 1 10.21037/jeccm.2017.09.02 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

