Optimization of Glycolipid Synthesis in Hydrophilic Deep Eutectic Solvents
- PMID: 32432093
- PMCID: PMC7214929
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00382
Optimization of Glycolipid Synthesis in Hydrophilic Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
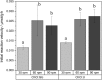
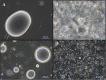
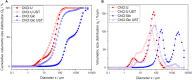
Glycolipids are considered an alternative to petrochemically based surfactants because they are non-toxic, biodegradable, and less harmful to the environment while having comparable surface-active properties. They can be produced chemically or enzymatically in organic solvents or in deep eutectic solvents (DES) from renewable resources. DES are non-flammable, non-volatile, biodegradable, and almost non-toxic. Unlike organic solvents, sugars are easily soluble in hydrophilic DES. However, DES are highly viscous systems and restricted mass transfer is likely to be a major limiting factor for their application. Limiting factors for glycolipid synthesis in DES are not generally well understood. Therefore, the influence of external mass transfer, fatty acid concentration, and distribution on initial reaction velocity in two hydrophilic DES (choline:urea and choline:glucose) was investigated. At agitation speeds of and higher than 60 rpm, the viscosity of both DES did not limit external mass transfer. Fatty acid concentration of 0.5 M resulted in highest initial reaction velocity while higher concentrations had negative effects. Fatty acid accessibility was identified as a limiting factor for glycolipid synthesis in hydrophilic DES. Mean droplet sizes of fatty acid-DES emulsions can be significantly decreased by ultrasonic pretreatment resulting in significantly increased initial reaction velocity and yield (from 0.15 ± 0.03 μmol glucose monodecanoate/g DES to 0.57 ± 0.03 μmol/g) in the choline: urea DES. The study clearly indicates that fatty acid accessibility is a limiting factor in enzymatic glycolipid synthesis in DES. Furthermore, it was shown that physical pretreatment of fatty acid-DES emulsions is mandatory to improve the availability of fatty acids.
Keywords: Candida antarctica lipase B; deep eutectic solvents; enzymatic synthesis; glycolipid; mass transfer; viscosity.
Copyright © 2020 Hollenbach, Bindereif, van der Schaaf, Ochsenreither and Syldatk.
Figures
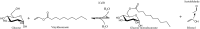


Similar articles
-
Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 18;21(12):4342. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124342. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32570792 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Eutectic Solvents as Suitable Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification Reactions.ChemSusChem. 2023 Oct 20;16(20):e202300615. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202300615. Epub 2023 Aug 9. ChemSusChem. 2023. PMID: 37423894
-
Microwave-Assisted One-Pot Lipid Extraction and Glycolipid Production from Oleaginous Yeast Saitozyma podzolica in Sugar Alcohol-Based Media.Molecules. 2021 Jan 18;26(2):470. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020470. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33477445 Free PMC article.
-
Parameters Influencing Lipase-Catalyzed Glycolipid Synthesis by (Trans-)Esterification Reaction.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2022;181:53-72. doi: 10.1007/10_2021_173. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34518911 Review.
-
Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biotechnology Applications.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2023 Jan;88(Suppl 1):S150-S175. doi: 10.1134/S0006297923140092. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2023. PMID: 37069119 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Eutectic Solvents and Multicomponent Reactions: Two Convergent Items to Green Chemistry Strategies.ChemistryOpen. 2021 Aug;10(8):815-829. doi: 10.1002/open.202100137. ChemistryOpen. 2021. PMID: 34402596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification.Molecules. 2025 Feb 7;30(4):778. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040778. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005090 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic synthesis of xylitol fatty acid esters in solvent-free conditions.Ultrason Sonochem. 2021 Jul;75:105606. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105606. Epub 2021 May 24. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021. PMID: 34058635 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial and Foaming Properties of Tailor-Made Glycolipids-Influence of the Hydrophilic Head Group and Functional Groups in the Hydrophobic Tail.Molecules. 2020 Aug 20;25(17):3797. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173797. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32825508 Free PMC article.
-
Lipase-Mediated Mechanoenzymatic Synthesis of Sugar Esters in Dissolved Unconventional and Neat Reaction Systems.ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022 Aug 8;10(31):10192-10202. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c01727. Epub 2022 Jul 27. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022. PMID: 35966390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker I. J. A., Matthews B., Suares H., Krodkiewska I., Furlong D. N., Grieser F., et al. (2000). Sugar fatty acid ester surfactants: structure and ultimate aerobic biodegradability. J. Surfactants Deterg. 3 1–11. 10.1007/s11743-000-0107-2 - DOI
-
- Bouzaouit N., Bidjou-haiour C. (2016). Response surface methodological study of glucose laurate synthesis catalyzed by immobilized lipase from candida cylindracea. Biol. Forum 8 420–427.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

