Recent Advances in Metabolically Engineered Microorganisms for the Production of Aromatic Chemicals Derived From Aromatic Amino Acids
- PMID: 32432104
- PMCID: PMC7214760
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00407
Recent Advances in Metabolically Engineered Microorganisms for the Production of Aromatic Chemicals Derived From Aromatic Amino Acids
Abstract
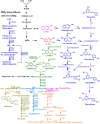
Aromatic compounds derived from aromatic amino acids are an important class of diverse chemicals with a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. They are currently produced via petrochemical processes, which are not sustainable and eco-friendly. In the past decades, significant progress has been made in the construction of microbial cell factories capable of effectively converting renewable carbon sources into value-added aromatics. Here, we systematically and comprehensively review the recent advancements in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology in the microbial production of aromatic amino acid derivatives, stilbenes, and benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. The future outlook concerning the engineering of microbial cell factories for the production of aromatic compounds is also discussed.
Keywords: aromatic amino acid derivatives; benzylisoquinoline alkaloids; metabolic engineering; microorganism; stilbenes; strain construction.
Copyright © 2020 Shen, Niu, Yan, Fong, Huang and Liu.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for bioproduction of value-added aromatic chemicals and natural products.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Oct;102(20):8685-8705. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9289-6. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30109397 Review.
-
Recent advances in microbial production of aromatic natural products and their derivatives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jan;102(1):47-61. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8599-4. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29127467 Review.
-
Biotechnological production of specialty aromatic and aromatic-derivative compounds.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 26;38(5):80. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03263-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35338395 Review.
-
Common problems associated with the microbial productions of aromatic compounds and corresponding metabolic engineering strategies.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Jul-Aug;41:107548. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107548. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 32289350 Review.
-
Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for production of aromatic compounds.Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Feb 26;18(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1090-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 30808357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improvement of betanin biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by metabolic engineering.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 12;8(1):54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.11.002. eCollection 2023 Mar. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36438069 Free PMC article.
-
From Biomass-Derived p-Hydroxycinnamic Acids to Novel Sustainable and Non-Toxic Phenolics-Based UV-Filters: A Multidisciplinary Journey.Front Chem. 2022 Jul 5;10:886367. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.886367. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35864863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for efficient l-tryptophan production.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 8;10(2):511-522. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.02.002. eCollection 2025 Jun. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40034180 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Sensors and Biosensors Modified with Conducting Polymers and Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Used in Electrochemical Detection of Amino Acids: Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, and Tryptophan.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 22;23(3):1218. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031218. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP and NADPH engineering of Escherichia coli to improve the production of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid using CRISPRi.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Apr 20;14(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13068-021-01954-6. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 33879249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bang H. B., Lee K., Lee Y. J., Jeong K. J. (2018). High-level production of trans-cinnamic acid by fed-batch cultivation of Escherichia coli. Process Biochem. 68, 30–36. 10.1016/j.procbio.2018.01.026 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

