A Case of Coronavirus Infection Incidentally Found on FDG PET/CT Scan
- PMID: 32433168
- PMCID: PMC7268833
- DOI: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003084
A Case of Coronavirus Infection Incidentally Found on FDG PET/CT Scan
Abstract
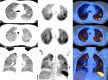
We present a highly suspicious case of COVID-19 infection, incidentally found on F-FDG PET/CT images. Patient was scanned on February, 25, 2020, when COVID-19 outbreak was unrecognized in our country. She admitted having recent occasional dry cough and fever. A retrospective review of her clinical and laboratory data was strongly suggestive for diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. PET/CT images demonstrated hypermetabolic diffuse ground glass opacities in both lungs with bilateral nodules. There was no evidence of pleural effusion or prominent mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy. Radiologists must be aware of COVID-19 presentations on PET/CT scan images during COVID-19 outbreak.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest and sources of funding: none declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FDG PET/CT in a Patient With Mantle Cell Lymphoma and COVID-19: Typical Findings.Clin Nucl Med. 2020 Jul;45(7):e305-e306. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003113. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32453077 Free PMC article.
-
Incidental Finding of COVID-19 Lung Infection in 18F-FDG PET/CT: What Should We Do?Clin Nucl Med. 2020 Aug;45(8):649-651. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003135. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32558722 Free PMC article.
-
18F-FDG PET/CT findings of COVID-19: a series of four highly suspected cases.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 May;47(5):1281-1286. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04734-w. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32088847 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic imaging findings in COVID-19].Ugeskr Laeger. 2020 Apr 6;182(15):V03200191. Ugeskr Laeger. 2020. PMID: 32286216 Review. Danish.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 Jul;215(1):87-93. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.23034. Epub 2020 Mar 14. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020. PMID: 32174129
Cited by
-
Effect of COVID-19 on 18F-FDG PET/CT: Is There a Need to Consider COVID-19 Status Before Planning 18F-FDG PET/CT for Oncologic Evaluation?J Nucl Med Technol. 2021 Sep;49(3):284-285. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.121.262145. Epub 2021 Jul 9. J Nucl Med Technol. 2021. PMID: 34244220 Free PMC article.
-
99mTc-Leukocyte Scintigraphy Revealed Viral Pulmonary Infection in a COVID-19 Patient.Clin Nucl Med. 2020 Oct;45(10):821-823. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003219. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32701817 Free PMC article.
-
Incidentally Detected COVID-19 Lung Changes during Oncologic Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography-Computerized Tomography Studies: Experience from Tertiary Care Cancer Hospital.Indian J Nucl Med. 2021 Oct-Dec;36(4):357-361. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_94_21. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Indian J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 35125752 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and Challenges in Molecular Imaging of Viral Infections.J Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 3;228(Suppl 4):S270-S280. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad247. J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37788495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical Presentation of COVID-19 Incidentally Detected at 18F-FDG PET/CT in an Asymptomatic Oncological Patient.Clin Nucl Med. 2020 Aug;45(8):e383-e385. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003175. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32520513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 51. World Health Organization (WHO). Available at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

