Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder clinical trial for percutaneous closure of the patent ductus arteriosus in patients ≥700 grams
- PMID: 32433821
- PMCID: PMC7754477
- DOI: 10.1002/ccd.28973
Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder clinical trial for percutaneous closure of the patent ductus arteriosus in patients ≥700 grams
Abstract
Objectives: Characterize the safety and effectiveness of the Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder for patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) closure.
Background: The presence of a hemodynamically significant PDA has been associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality in children born premature.
Methods: This was a single arm, prospective, multicenter, non-randomized study to evaluate the Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder to treat PDA in patients ≥700 g. From June 2017 to February 2019, 200 patients were enrolled at nine centers, with 100 patients weighing ≤2 kg. Primary effectiveness endpoint was the rate of PDA closure at 6-month follow-up. Primary safety endpoint was the rate of major complications through 6 months. Secondary endpoint was rate of significant pulmonary or aortic obstruction through 6 months' follow-up.
Results: The implant success rate was 95.5% (191/200) overall and 99% in patients ≤2 kg (99/100). The primary effectiveness endpoint was achieved in 99.4% of implanted patients. Four patients experienced a primary safety endpoint event (2 transfusions, 1 hemolysis, and 1 aortic obstruction). There were no branch pulmonary artery obstructions. Five patients, all ≤2 kg, were noted to have worsening of tricuspid regurgitation (TR) after the procedure. None of the TR incidences manifested clinically. The Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder received FDA approval in January 2019 and became the first device approved for PDA closure in patients ≥700 g.
Conclusions: This study supports the safety and effectiveness of the Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder, particularly in patients between 700 g and 2 kg where there is currently a significant unmet need in the United States. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03055858.
Keywords: ADO II AS; Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder; FDA; patent ductus arteriosus; prematurity; transcatheter closure.
© 2020 The Authors. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Sathanandam: proctor/consultant Abbott; D. Gutfinger: full‐time employee Abbott; L. O'Brien: full‐time Abbott employee; T. Forbes: proctor/consultant Abbott, Edwards, AcuNav/Biosence Webster, B. Braun Medical, Siemens, Medtronic; M. Gillespie: proctor/consultant Abbott; D. Berman: proctor/consultant Abbott, Edwards, Medtronic; A. Armstrong: proctor/consultant Abbott, Edwards, Medtronic, B. Braun; S. Shahanavaz: proctor Abbott, Medtronic, and Edwards; T. Jones: research grant, proctor/consultant Abbott, Edwards, Medtronic, W.L. Gore & Assoc.; B. Morray: Consultant Medtronic, proctor Abbott; T. Rockefeller: proctor Abbott; H. Justino: proctor/consultant Abbott, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic; Clinical trial executive committee Janssen Pharmaceutical; Co‐founder PolyVascular; scientific advisory board Pediastent; D. Nykanen: proctor Abbott, consultant and independent data reviewer W.L. Gore & Assoc, expert witness Glaxo Smith Kline; E. Zahn: consultant/proctor Abbott, Edwards, Medtronic, National PI ADO II AS IDE Trial and Alterra/S3.
Figures
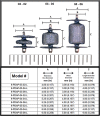
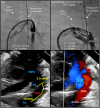



References
-
- Hamrick SE, Hansmann G. Patent ductus arteriosus of the preterm infant. Pediatrics. 2010;125(5):1020‐1030. - PubMed
-
- Gersony WM. Patent ductus arteriosus in the neonate. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986;33:545‐560. - PubMed
-
- Jim WT, Chiu NC, Chen MR, et al. Cerebral hemodynamic change and intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005;31:197‐202. - PubMed
-
- Koehne PS, Bein G, Alexi‐Meskhishvili V, Weng Y, Bührer C, Obladen M. Patent ductus arteriosus in very low birthweight infants: complications of pharmacological and surgical treatment. J Perinat Med. 2001;29(4):327‐334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

