CD5 signalosome coordinates antagonist TCR signals to control the generation of Treg cells induced by foreign antigens
- PMID: 32434911
- PMCID: PMC7293642
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1917182117
CD5 signalosome coordinates antagonist TCR signals to control the generation of Treg cells induced by foreign antigens
Abstract
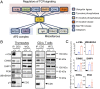
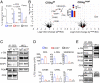
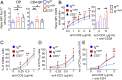
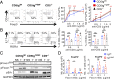
CD5 is characterized as an inhibitory coreceptor with an important regulatory role during T cell development. The molecular mechanism by which CD5 operates has been puzzling and its function in mature T cells suggests promoting rather than repressing effects on immune responses. Here, we combined quantitative mass spectrometry and genetic studies to analyze the components and the activity of the CD5 signaling machinery in primary T cells. We found that T cell receptor (TCR) engagement induces the selective phosphorylation of CD5 tyrosine 429, which serves as a docking site for proteins with adaptor functions (c-Cbl, CIN85, CRKL), connecting CD5 to positive (PI3K) and negative (UBASH3A, SHIP1) regulators of TCR signaling. c-CBL acts as a coordinator in this complex enabling CD5 to synchronize positive and negative feedbacks on TCR signaling through the other components. Disruption of CD5 signalosome in mutant mice reveals that it modulates TCR signal outputs to selectively repress the transactivation of Foxp3 and limit the inopportune induction of peripherally induced regulatory T cells during immune responses against foreign antigen. Our findings bring insights into the paradigm of coreceptor signaling, suggesting that, in addition to providing dualistic enhancing or dampening inputs, coreceptors can engage concomitant stimulatory and inhibitory signaling events, which act together to promote specific functional outcomes.
Keywords: T cells; coreceptors; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD5 expression is developmentally regulated by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and TCR avidity.J Exp Med. 1998 Dec 21;188(12):2301-11. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.12.2301. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9858516 Free PMC article.
-
CD5 plays an inhibitory role in the suppressive function of murine CD4(+) CD25(+) T(reg) cells.Immunol Lett. 2008 Aug 15;119(1-2):103-13. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.05.008. Epub 2008 Jun 23. Immunol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18573278 Free PMC article.
-
Fine tuning of TCR signaling by CD5.J Immunol. 2001 May 1;166(9):5464-72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.9.5464. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11313384
-
CD5, an Undercover Regulator of TCR Signaling.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 7;9:2900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02900. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30581443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD6, a Rheostat-Type Signalosome That Tunes T Cell Activation.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 18;9:2994. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02994. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omic analyses of changes in the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma following neoadjuvant treatment with anti-PD-1 therapy.Cancer Cell. 2022 Nov 14;40(11):1374-1391.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Cancer Cell. 2022. PMID: 36306792 Free PMC article.
-
[CBL inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells by ubiquitylation-mediated degradation of NCK2].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Nov 20;42(11):1594-1603. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.11.02. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36504051 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Gene variation impact on prostate cancer progression: Lymphocyte modulator, activation, and cell adhesion gene variant contribution.Prostate. 2022 Oct;82(14):1331-1337. doi: 10.1002/pros.24407. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Prostate. 2022. PMID: 35767366 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile CRISPR-Cas13d platform for multiplexed transcriptomic regulation and metabolic engineering in primary human T cells.Cell. 2024 Feb 29;187(5):1278-1295.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.035. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38387457 Free PMC article.
-
CD5 Deficiency Alters Helper T Cell Metabolic Function and Shifts the Systemic Metabolome.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 18;10(3):704. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030704. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coquet J. M., Rausch L., Borst J., The importance of co-stimulation in the orchestration of T helper cell differentiation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 93, 780–788 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Acuto O., Michel F., CD28-mediated co-stimulation: A quantitative support for TCR signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 939–951 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Parry R. V., Riley J. L., Ward S. G., Signalling to suit function: Tailoring phosphoinositide 3-kinase during T-cell activation. Trends Immunol. 28, 161–168 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

