Enzyme-mediated depletion of serum l-Met abrogates prostate cancer growth via multiple mechanisms without evidence of systemic toxicity
- PMID: 32434918
- PMCID: PMC7293657
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1917362117
Enzyme-mediated depletion of serum l-Met abrogates prostate cancer growth via multiple mechanisms without evidence of systemic toxicity
Abstract
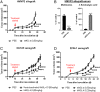
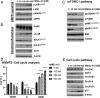
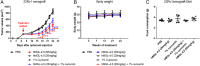
Extensive studies in prostate cancer and other malignancies have revealed that l-methionine (l-Met) and its metabolites play a critical role in tumorigenesis. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that systemic restriction of serum l-Met, either via partial dietary restriction or with bacterial l-Met-degrading enzymes exerts potent antitumor effects. However, administration of bacterial l-Met-degrading enzymes has not proven practical for human therapy because of problems with immunogenicity. As the human genome does not encode l-Met-degrading enzymes, we engineered the human cystathionine-γ-lyase (hMGL-4.0) to catalyze the selective degradation of l-Met. At therapeutically relevant dosing, hMGL-4.0 reduces serum l-Met levels to >75% for >72 h and significantly inhibits the growth of multiple prostate cancer allografts/xenografts without weight loss or toxicity. We demonstrate that in vitro, hMGL-4.0 causes tumor cell death, associated with increased reactive oxygen species, S-adenosyl-methionine depletion, global hypomethylation, induction of autophagy, and robust poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage indicative of DNA damage and apoptosis.
Keywords: hMGL; l-methionine depletion; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: W.-C.L., G.G., and E.S. are inventors on intellectual property related to this work, and G.G. and E.S. have an equity interest in Aeglea Biotherapeutics, a company that has licensed the commercial development of hMGL-4.0.
Figures


Comment in
-
Uro-Science.J Urol. 2021 Apr;205(4):1228-1229. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001605. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33472375 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aki T. et al. ., Evaluation of brain tumors using dynamic 11C-methionine-PET. J. Neurooncol. 109, 115–122 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Tang B. N. et al. ., Three-dimensional Gaussian model to define brain metastasis limits on 11C-methionine PET. Radiother. Oncol. 89, 270–277 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Tóth G., et al. , Detection of prostate cancer with 11C-methionine positron emission tomography. J. Urol. 173, 66–69, discussion 69 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Kaste S. C. et al. ., Comparison of 11C-methionine and 18F-FDG PET/CT for staging and follow-up of pediatric lymphoma. J. Nucl. Med. 58, 419–424 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

