Inhibiting Airway Smooth Muscle Contraction Using Pitavastatin: A Role for the Mevalonate Pathway in Regulating Cytoskeletal Proteins
- PMID: 32435188
- PMCID: PMC7218099
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00469
Inhibiting Airway Smooth Muscle Contraction Using Pitavastatin: A Role for the Mevalonate Pathway in Regulating Cytoskeletal Proteins
Abstract
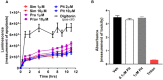
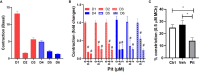
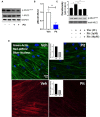
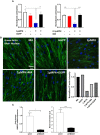
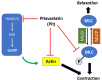
Despite maximal use of currently available therapies, a significant number of asthma patients continue to experience severe, and sometimes life-threatening bronchoconstriction. To fill this therapeutic gap, we examined a potential role for the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) inhibitor, pitavastatin. Using human airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells and murine precision-cut lung slices, we discovered that pitavastatin significantly inhibited basal-, histamine-, and methacholine (MCh)-induced ASM contraction. This occurred via reduction of myosin light chain 2 (MLC2) phosphorylation, and F-actin stress fiber density and distribution, in a mevalonate (MA)- and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP)-dependent manner. Pitavastatin also potentiated the ASM relaxing effect of a simulated deep breath, a beneficial effect that is notably absent with the β2-agonist, isoproterenol. Finally, pitavastatin attenuated ASM pro-inflammatory cytokine production in a GGPP-dependent manner. By targeting all three hallmark features of ASM dysfunction in asthma-contraction, failure to adequately relax in response to a deep breath, and inflammation-pitavastatin may represent a unique asthma therapeutic.
Keywords: asthma; bronchodilation; inflammation; mechanics; mechanopharmacology; mevalonate; statin; stretch.
Copyright © 2020 Lu, Zeki, Ram-Mohan, Nguyen, Bai, Chmiel, Pecic, Ai, Krishnan and Ghosh.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pitavastatin, a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, blocks vascular smooth muscle cell populated-collagen lattice contraction.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2004 Jun;43(6):808-14. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200406000-00010. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15167274
-
Interval between simulated deep inspirations on the dynamics of airway smooth muscle contraction in guinea pig bronchi.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;259:136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30217723
-
Comparison of gel contraction mediated by airway smooth muscle cells from patients with and without asthma.Thorax. 2007 Oct;62(10):848-54. doi: 10.1136/thx.2006.070474. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Thorax. 2007. PMID: 17412779 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Airway Smooth Muscle Contraction in Health and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1124:381-422. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-5895-1_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31183836 Review.
-
Deep inspiration and airway smooth muscle adaptation to length change.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2003 Sep 16;137(2-3):169-78. doi: 10.1016/s1569-9048(03)00145-9. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14516724 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting cytoskeletal biomechanics to modulate airway smooth muscle contraction in asthma.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jan;301(1):108028. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108028. Epub 2024 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39615690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

