IGFBP-1 Expression Promotes Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells via Erk Pathway Activation
- PMID: 32435229
- PMCID: PMC7218143
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00233
IGFBP-1 Expression Promotes Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells via Erk Pathway Activation
Abstract
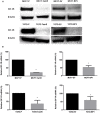
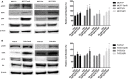
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system plays a significant role in many cellular processes, including proliferation, and survival. In estrogen receptor positive breast cancer, the level of circulating IGF-1 is positively associated with the incidence and at least 50% of cases have elevated IGF-1R signaling. Tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator and antagonist for estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in breast tissue, is a commonly prescribed adjuvant treatment for patients presenting with ERα-positive breast cancer. Unfortunately, tamoxifen resistance is a frequent occurrence in patients receiving treatment and the molecular mechanisms that underlie tamoxifen resistance not adequately defined. It has recently been reported that the inhibition of IGF-1R activation and the proliferation of breast cancer cells upon tamoxifen treatment is mediated by the accumulation of extracellular insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1). Elevated IGFBP-1 expression was observed in tamoxifen-resistant (TamR) MCF-7 and T-47D cells lines suggesting that the tamoxifen-resistant state is associated with IGFBP-1 accumulation. MCF-7 and T-47D breast cancer cells stably transfected with and IGFBP-1 expression vector were generated (MCF7-BP1 and T47D-BP1) to determine the impact of breast cancer cell culture in the presence of increased IGFBP-1 expression. In these cells, the expression of IGF-1R was significantly reduced compared to controls and was similar to our observations in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 and T-47D cells. Also similar to TamR breast cancer cells, MCF7-BP1 and T47D-BP1 were resistant to tamoxifen treatment, had elevated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression, increased phospho-EGFR (pEGFR), and phospho-Erk (pErk). Furthermore, tamoxifen sensitivity was restored in the MCF7-BP1 and T47D-BP1 upon inhibition of Erk phosphorylation. Lastly, the transient knockdown of IGFBP-1 in MCF7-BP1 and T47D-BP1 inhibited pErk accumulation and increased tamoxifen sensitivity. Taken together, these data support the conclusion that IGFBP-1 is a key component of the development of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells.
Keywords: EGFR; IGFBP-1; breast cancer; drug resistance; tamoxifen.
Copyright © 2020 Zheng, Sowers and Houston.
Figures





Similar articles
-
IGF-1 Receptor Modulates FoxO1-Mediated Tamoxifen Response in Breast Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Apr;15(4):489-497. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0176. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28096479 Free PMC article.
-
[Involvement of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in tamoxifen resistance of MCF-7 cells].Ai Zheng. 2006 Jul;25(7):839-43. Ai Zheng. 2006. PMID: 16831274 Chinese.
-
Androgen receptor promotes tamoxifen agonist activity by activation of EGFR in ERα-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Nov;154(2):225-37. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3609-7. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26487496 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen signals via an extra-nuclear pathway involving IGF-1R and EGFR in tamoxifen-sensitive and -resistant breast cancer cells.Steroids. 2009 Jul;74(7):586-94. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2008.11.020. Epub 2008 Dec 7. Steroids. 2009. PMID: 19138696 Review.
-
MAPK signaling mediates tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 May 23. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05304-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40410609 Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling Pathways of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins.Endocr Rev. 2023 Sep 15;44(5):753-778. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad008. Endocr Rev. 2023. PMID: 36974712 Free PMC article.
-
A bioinformatic study of IGFBPs in glioma regarding their diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic prediction value.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Mar 15;15(3):2140-2155. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37056850 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 modulates proliferative antagonism in response to progesterone in breast cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 4;15:1450648. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1450648. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39698031 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNA-363 during tumor progression and invasion.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 Aug;80(3):481-499. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01022-1. Epub 2024 May 1. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38691273 Review.
-
Insulin‑like growth factor in cancer: New perspectives (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Aug;32(2):209. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13574. Epub 2025 May 26. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40417926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

