Improving the Potency of N-Aryl-2,5-dimethylpyrroles against Multidrug-Resistant and Intracellular Mycobacteria
- PMID: 32435364
- PMCID: PMC7236041
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00515
Improving the Potency of N-Aryl-2,5-dimethylpyrroles against Multidrug-Resistant and Intracellular Mycobacteria
Abstract
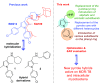
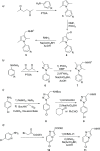
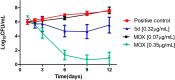
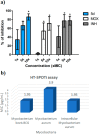
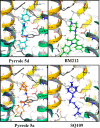
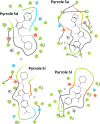
A series of N-phenyl-2,5-dimethylpyrrole derivatives, designed as hybrids of the antitubercular agents BM212 and SQ109, have been synthesized and evaluated against susceptible and drug-resistant mycobacteria strains. Compound 5d, bearing a cyclohexylmethylene side chain, showed high potency against M. tuberculosis including MDR-TB strains at submicromolar concentrations. The new compound shows bacteriostatic activity and low toxicity and proved to be effective against intracellular mycobacteria too, showing an activity profile similar to isoniazid.
Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance, 2014. https://www.who.int/drugresistance/documents/surveillancereport/en (December 10, 2019).
-
- Fox W.; Ellard G. A.; Mitchison D. A. Studies on the treatment of tuberculosis undertaken by the British Medical Research Council Tuberculosis Units, 1946–1986, with relevant subsequent publications. Int. J. Tuberc Lung Dis. 1999, 3, 231–279. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Tuberculosis. http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (December 2, 2019).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

