Effect of different coloring techniques and surface treatment methods on the surface roughness of monolithic zirconia
- PMID: 32435439
- PMCID: PMC7224263
Effect of different coloring techniques and surface treatment methods on the surface roughness of monolithic zirconia
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the effect of different coloring techniques and surface treatment methods on the surface roughness of monolithic zirconia ceramic.
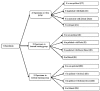
Materials and methods: In this in vitro study seventy-two disk-shaped monolithic zirconia (2 mm × 10 mm) were divided into three coloring techniques groups (white, internal staining, external staining) (n = 24). Each group was subdivided into four surface treatment subgroups (n = 6), as unpolished, polished with Shofu polishing kit, polished with dental direct polishing kit, and glazed. Profilometer was used to measure the Ra (roughness average) and Rz (roughness height) surface roughness values (μm) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for visual inspection of the surface morphology. The surface roughness parameters were calculated and analyzed with two-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test (α = 0.05).
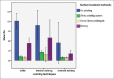
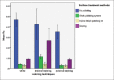
Results: The coloring technique, surface treatment method, and interaction of these two parameters significantly affected the Ra and Rz parameters (P < 0.05). Concerning the surface treatment, the Rz value was significantly higher in the unpolished subgroup, followed by the glazed and polished subgroups. However, the two polishing systems were not significantly different. The internal staining group had significantly higher Rz value than the other staining method, when the specimens were glazed or polished with Shofu kit. SEM showed multiple scratches in unpolished samples which were smoothened by glazing and specially by polishing.
Conclusion: Among all the studied surface treatment methods, the lowest surface roughness was observed in highly polished monolithic zirconia, which was even less than the glazed one. The internal staining method can create a rougher surface for some of the surface treatment methods.
Keywords: Ceramic; prosthesis coloring; staining; zirconia.
Copyright: © 2020 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
Figures


References
-
- Rosenstiel SF, Land MF, Fujimoto J. Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics-E-Book. St. Louis: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2015.
-
- Denry I, Kelly JR. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent Mater. 2008;24:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Conrad HJ, Seong WJ, Pesun IJ. Current ceramic materials and systems with clinical recommendations: A systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2007;98:389–404. - PubMed
-
- Torabi Ardakani M, Giti R, Taghva M, Javanmardi S. Effect of a zirconia primer on the push-out bond strength of zirconia ceramic posts to root canal dentin. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;114:398–402. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
