Inhibition of IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway to improve Dasatinib efficacy in suppression of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32435511
- PMCID: PMC7229171
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-020-0270-7
Inhibition of IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway to improve Dasatinib efficacy in suppression of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
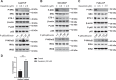
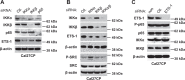
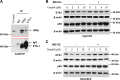
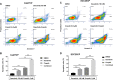
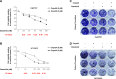
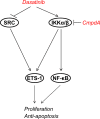
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src plays an important role in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). However, the FDA-approved SRC inhibitor Dasatinib shows very limited efficacy in HNSCC clinical trials, even though Dasatinib can completely inhibit SRC in the laboratory setting. These results suggest that SRC inhibition can cause compensatory up-regulation and/or activation of other survival pathways, which suggests that co-targeting of SRC and the potential signaling pathways may improve the Dasatinib efficacy. In this study, we investigated the role of IKKβ/NF-κB in regulation of the sensitivity of cisplatin-resistant HNSCC to Dasatinib. Additionally, we wished to determine whether inhibition of the IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway could enhance Dasatinib efficacy to inhibit cisplatin-resistant HNSCC without the use of cisplatin. Previous studies have shown that ETS-1 is a crucial SRC effector protein that regulates cancer cell proliferation, anti-apoptosis, and metastasis. We found that SRC kinase inhibition by Dasatinib decreased ETS-1 expression but caused elevation of IKKβ/NF-κB signaling in multiple cisplatin-resistant HNSCC. Interestingly, inhibition of IKKβ/NF-κB by CmpdA (Bay65-1942), a recently identified IKKβ inhibitor, also led to a decrease in ETS-1 levels. Moreover, the knockdown of IKK, but not NF-κB, dramatically decreased ETS-1 expression. In addition, IKKβ and ETS-1 interacted in cisplatin-resistant HNSCC. These data demonstrated cross-talk between SRC and IKK to regulate NF-κB and ETS-1. Furthermore, we found that simultaneous inhibition of SRC and IKKβ through a Dasatinib and CmpdA combination synergistically inhibited NF-κB activation and ETS-1expression, suppressed cell proliferation, and induced apoptosis. Taken together, our data indicate that SRC and IKKβ play crucial roles in cisplatin-resistant HNSCCC and co-targeting SRC and IKKβ could be an effective strategy to treat cisplatin-resistant HNSCC.
Keywords: Targeted therapies; Translational research.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the SRC/ETS-1 signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2019 May 22;19(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5664-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31118072 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of migration, invasion, and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through IKKβ inhibition.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Apr;37(2):283-292. doi: 10.1007/s10585-020-10021-7. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 32020377 Free PMC article.
-
IKK phosphorylation of NF-κB at serine 536 contributes to acquired cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Sep 15;5(10):3098-110. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26693062 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Targeting IKKβ in Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities for the Therapeutic Utilisation of IKKβ Inhibitors.Cells. 2018 Aug 23;7(9):115. doi: 10.3390/cells7090115. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30142927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of HPV in Mexican Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma and Identification of Potential Prognostic Biomarkers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;13(22):5602. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225602. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830760 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the prognostic potential of a necroptosis-related gene signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a bioinformatic analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 31;14(1):340-353. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-743. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39974401 Free PMC article.
-
Head and neck cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 21;5(9):e702. doi: 10.1002/mco2.702. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39170944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-485-5p targets keratin 17 to regulate oral cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the integrin/FAK/Src/ERK/β-catenin pathway.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Jun 15;29(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00824-z. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 35706019 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term zinc treatment alters the mechanical properties and metabolism of prostate cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Sep 11;24(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03495-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39261823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seeburg, D. P., Baer, A. H. & Aygun, N. Imaging of patients with head and neck cancer: from staging to surveillance. Oral Maxil. Surg. Clin. N. Am., 10.1016/j.coms.2018.06.004 (2018). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

