Heart Retransplantation: Candidacy, Outcomes, and Management
- PMID: 32435573
- PMCID: PMC7223608
- DOI: 10.1007/s40472-019-00257-y
Heart Retransplantation: Candidacy, Outcomes, and Management
Abstract
Purpose of review: To describe the incidence and epidemiology of heart retransplantation in adults and children and to review the risk factors associated with adverse outcome following retransplantation to help guide recipient selection.
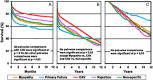
Recent findings: Heart retransplantation is associated with inferior short-term and long-term survival when compared with primary heart transplantation and its use remains controversial although less so in the pediatric heart transplant population.
Summary: In the most recent era of heart transplantation, patients retransplanted for CAV, greater than 1 year from their primary transplant, and who are not in critical condition have improved survival compared with other retransplant recipients. Survival with retransplantation can approach that of primary transplantation when patients are appropriately selected. More research is needed regarding the optimal timing for retransplantation and the optimal management for patients after retransplantation.
Keywords: Advanced heart failure; Heart transplant; Retransplantation.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestMaya Barghash declares no conflict of interest. Sean Pinney reports personal fees from Abbott Inc, Alnylam Inc., Medtronic Inc., and Procyrion Inc., outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology, risk factors, and outcomes of lung retransplantation: An analysis of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Thoracic Transplant Registry.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2022 Oct;41(10):1478-1486. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2022.06.022. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35933297 Free PMC article.
-
Retransplant and Medical Therapy for Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy: International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Registry Analysis.Am J Transplant. 2016 Jan;16(1):301-9. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13418. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Am J Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26274617
-
Long-term survival after retransplantation of the liver.Ann Surg. 1997 Oct;226(4):408-18; discussion 418-20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199710000-00002. Ann Surg. 1997. PMID: 9351709 Free PMC article.
-
To transplant or not to transplant recurrent hepatitis C and liver failure.Clin Liver Dis. 2003 Aug;7(3):615-29. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(03)00053-9. Clin Liver Dis. 2003. PMID: 14509530 Review.
-
Lung retransplantation in the modern era.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Nov;13(11):6587-6593. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2021-25. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34992837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimal patient selection for simultaneous heart-kidney transplant: A modified cost-effectiveness analysis.Am J Transplant. 2022 Apr;22(4):1158-1168. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16888. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34741786 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic Valve Replacement and Tricuspid Valve Repair Five Years After Orthotopic Heart Transplantation in an Adult Patient.Cureus. 2023 Sep 4;15(9):e44688. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44688. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37809256 Free PMC article.
-
Heart retransplant recipients with renal dysfunction benefit from simultaneous heart-kidney transplantation.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2023 Aug;42(8):1045-1053. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2023.04.010. Epub 2023 Apr 23. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37098375 Free PMC article.
-
Transition to Advanced Heart Failure: From Identification to Improving Prognosis.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Mar 17;12(3):104. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12030104. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40137102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography in the Assessment and Management of Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024 Aug;26(8):777-782. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02078-7. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38864982 Review.
References
-
- Khush KK, et al. for the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT): thirty-fifth Adult Heart and Lung Transplantation Report – 2018; Focus Theme: Multiorgan Transplantation. JHLT. 2018;30(10):1155–1168. - PubMed
-
- • Lund LH et al. for the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation. The registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-first official adult heart transplant report – 2014; focus theme: Retransplantation. JHLT 2014; 33(10): 996-1008. This ISHLT report from the international registry focused on providing data on adult heart retransplantation. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava Rohit, Keck Berkeley M., Bennett Leah E., Hosenpud Jeffrey D. THE RESULTS OF CARDIAC RETRANSPLANTATION: AN ANALYSIS OF THE JOINT INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR HEART AND LUNG TRANSPLANTATION/UNITED NETWORK FOR ORGAN SHARING THORACIC REGISTRY. Transplantation. 2000;70(4):606–612. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200008270-00013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Costanzo MR, Naftel DC, Pritzker MR, Heilman JK, Boehmer JP, Brozena SC, et al. Heart transplant coronary artery disease detected by coronary angiography: a multiinstitutional study of preoperative donor and recipient risk factors. Cardiac transplant research database. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1998;17:744–75. - PubMed
-
- Mehra Mandeep R., Crespo-Leiro Maria G., Dipchand Anne, Ensminger Stephan M., Hiemann Nicola E., Kobashigawa Jon A., Madsen Joren, Parameshwar Jayan, Starling Randall C., Uber Patricia A. International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation working formulation of a standardized nomenclature for cardiac allograft vasculopathy—2010. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2010;29(7):717–727. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2010.05.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
